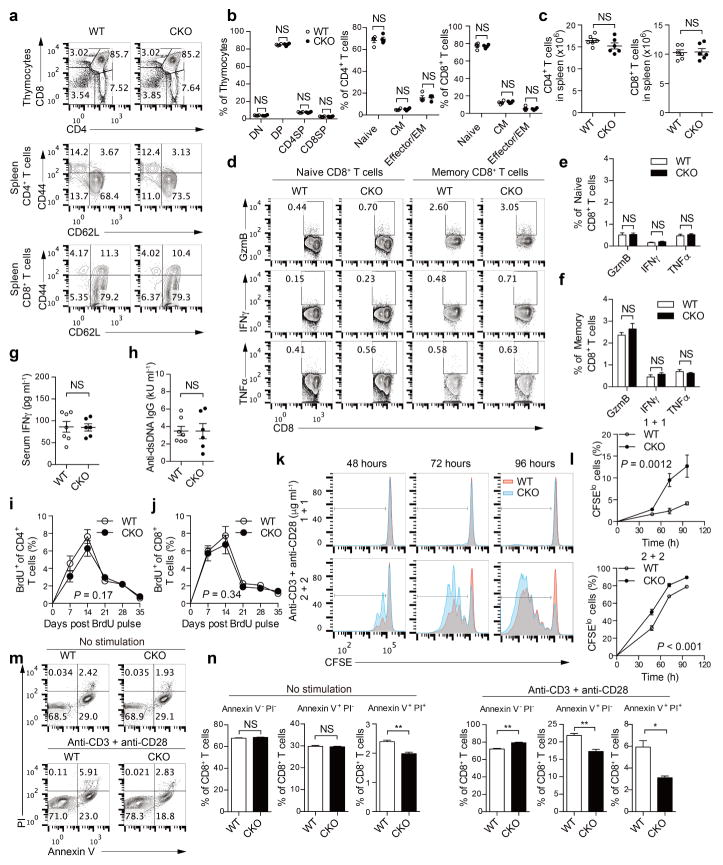
Extended Data Figure 3. ACAT1 deficiency does not affect thymocyte development and peripheral T-cell homeostasis, but results in enhanced proliferation and reduced apoptosis of CD8+ T cells.
a, b, Flow cytometric analysis of thymocytes and splenic T cells from wild-type and CKO mice (8 weeks old, n = 4). Representative flow cytometric profiles were shown in a. Percentages of CD4− CD8− double negative (DN), CD4+ CD8+ double positive (DP), CD4+ single positive (CD4SP) and CD8+ single positive (CD8SP) cells in total thymocytes were comparable (b, left). Naive (CD44loCD62Lhi), central memory (CD44hiCD62Lhi; CM) and effector/effector memory (CD44hi CD62Llo, effector/EM) of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells from the spleen of wild-type and CKO mice were comparable (b, right). Data were analysed by Mann–Whitney test, and no significant difference was observed. c, Total CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell numbers from the spleen of wild-type and CKO mice (8 weeks old, n = 6) were assessed using flow cytometry. Data were analysed with Mann–Whitney test, and no significant difference was observed. d–f, Cytokine/granule productions of resting naive (CD62LhiCD44lo) and central memory (CD62LhiCD44hi) CD8+ T cells from the spleen of wild-type and CKO mice (8 weeks old, n = 3). CD8 + T cells were isolated from the spleen and cultured for 4 h in the presence of 5 μg ml−1 brefeldin A. Naive and memory populations were gated by CD62L and CD44 expression. Data were analysed by unpaired t-test, and no significant difference was observed. g, h, Serum levels of IFNγ and auto-antibody anti-dsDNA IgG of wild-type and CKO mice (12 weeks old, WT, n = 7; CKO, n = 6) were assessed using ELISA. Data were analysed by Mann–Whitney test, and no significant difference was observed. i, j, T-cell homeostasis was measured by BrdU labelling and detection. Wild-type and CKO mice (6 weeks old) were injected with a single dose (2 mg) of BrdU intraperitoneally. Peripheral blood was collected at the indicated time and analysed using flow cytometry. Percentages of BrdU+ cells in total peripheral CD4+ and CD8+ T cells of wild-type and CKO mice (n = 6) were plotted. Data were analysed by two-way ANOVA, and no significant difference was observed. k, l, CD8+ T-cell proliferation was measured by CFSE dilution. Cells were stimulated with 1–2 μg ml−1 plate-bound anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 antibodies for the indicated time. Data were analysed by two-way ANOVA (n = 3). m, n, CD8+ T-cell apoptosis was measured by annexin V and propidium iodide (PI) staining. The naive CD8+ cells were isolated from the spleen of wild-type or CKO mice (8 weeks old), and cultured in medium for 24 h without stimulation, or stimulated with 5 μg ml−1 plate-bound anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 antibodies for 24 h. Annexin V and propidium iodide were used to stain early (annexin V+ PI−) and late (annexin V+ PI+) cells apoptotic. Apoptotic cells were significantly lower in CKO CD8+ T cells than in wild-type CD8+ T cells. Data were analysed by unpaired t-test (n = 3). Error bars denote s.e.m; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.