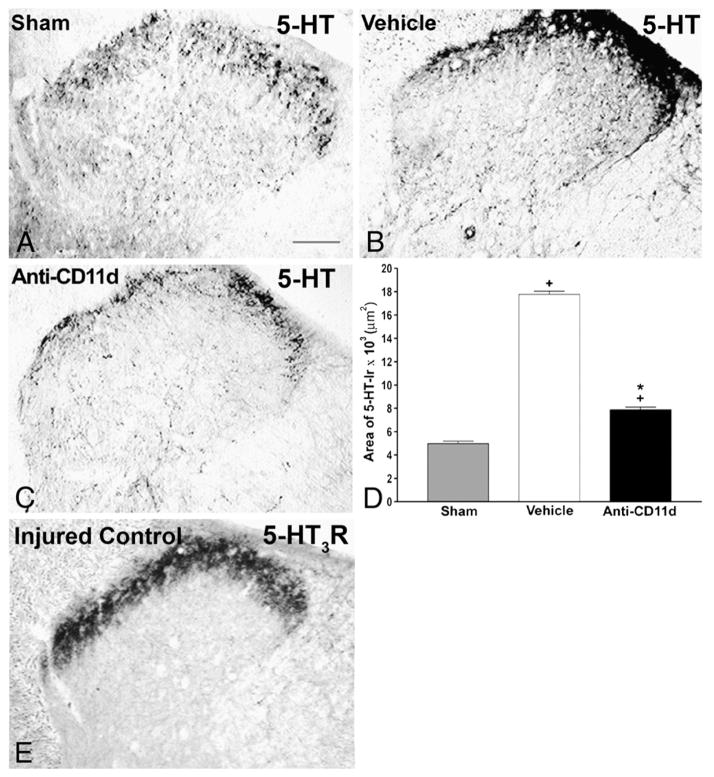
Fig. 4.
Serotonin (5-HT) immunoreactivity in laminae I–IV of the dorsal horn rostral to a T12 spinal cord injury 4 weeks after the injury. A–C) Photomicrographs of transverse sections of the dorsal horn in sham-injured, vehicle-treated, and anti-CD11d mAb-treated rats. After SCI, the distribution and density of 5-HTimmunoreactive fibers were increased significantly, primarily in the superficial laminas, with punctate fibers in laminas III and IV. Anti-CD11d mAb treatment normalized the distribution of 5-HT-immunoreactive fibers toward patterns observed in sham-injured animals. Scale bar, 100 μm. D) The area of 5-HT-immunoreactivity in the dorsal horn rostral to the injury at T12–13 presented as the mean area±SE of 5-HT-immunoreactivity in the sham injured (n=6), vehicle-treated (n=5), and anti-CD11d mAb-treated (n=6) groups. *, P<0.05 compared with vehicle-treated rats; +, P<0.05 compared with sham-injured rats. E) Photomicrograph of 5-HT3-R-immunoreactivity in a transverse section from the 9th thoracic segment of a rat injured at T12. Immunoreactivity is primarily localized within the superficial laminae I and II of the dorsal horn with sparse amounts in the deeper laminae. Scale bar=100 μm (A) refers to all sections.
Adapted, with permission, from Oatway et al. (2005).