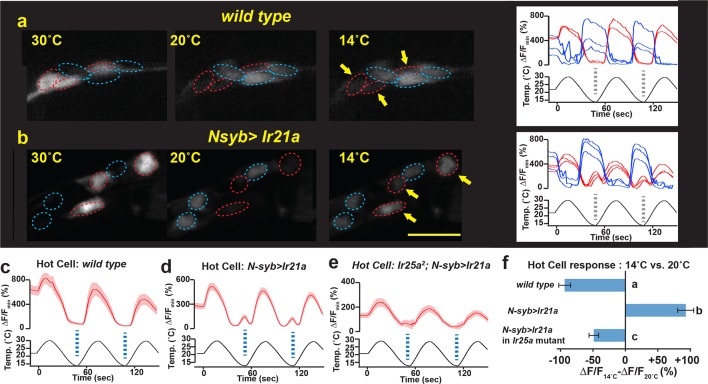
Figure 5. IR21a expression confers cool-sensitivity upon warmth-responsive Hot Cell neurons.
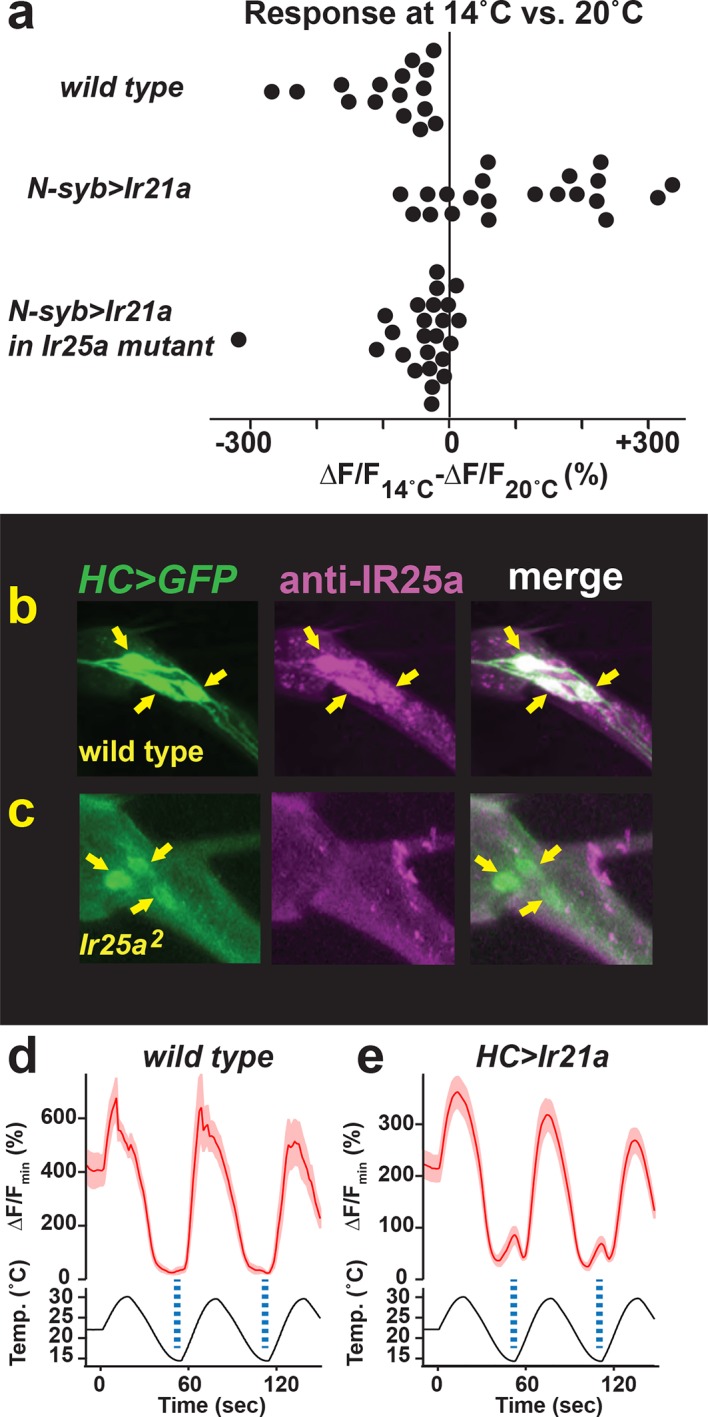
(a,b) Temperature responses of wild type (a) or N-syb>Ir21a-expressing (b) thermoreceptors in the arista, monitored with N-syb>GCaMP6m. Cell bodies of warmth-responsive Hot Cells outlined in red and cool-responsive Cold Cells in blue. Arrows highlight Hot Cells at 14˚C. Traces of Hot Cell and Cold Cell responses shown at right. Scale bar, 10 microns. (c-e) Fluorescence of Hot Cells in response to sinusoidal 14˚C to 30˚C temperature stimulus, quantified as percent ∆F/Fmin. Dotted lines denote temperature minima. Traces, average +/- SEM. (f) Difference between ∆F/Fmin at 14˚C vs 20˚C (average +/- SEM). Responses of N-syb>Ir21a cells were statistically distinct from both wild type and Ir25a2;N-syb>Ir21a (p<0.01, Steel-Dwass test; letters denote statistically distinct groups). wild type, n= 16 cells (from 8 animals). N-syb>Ir21a, n= 16 (10). Ir25a2; N-syb>Ir21a, n= 20 (10). Analysis of endogenous IR25a expression in the Hot Cells and of the consequences of Hot Cell-specific misexpression of IR21a provided in Figure 5—figure supplement 1.
Figure 5—figure supplement 1. Hot Cell neurons express IR25a protein, and IR21a confers cool-sensitivity upon the Hot Cell neurons.