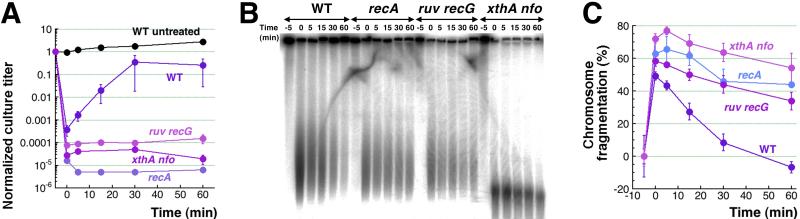
Fig. 6. Recombinational repair of CN + H2O2-induced double-strand breaks.
A. Kinetics of survival/’revival’ after 3 mM CN + 2 mM H2O2 treatment. After 5 minutes of treatment, CN and H2O2 were removed by pelleting cells by centrifugation, resuspending in fresh LB and allowing to recover at 37°C. Repair-deficient mutants, such as recA, recG ruvABC and xthA nfo, were included as negative controls. Growth of the untreated WT culture was also monitored in parallel.
B. A representative pulsed-field gel showing the disappearance of catastrophic chromosomal fragmentation in WT cells induced by 5-minute CN + H2O2 treatment, upon removal of the treatment at time = 0. In contrast, recA, recG ruvABC and xthA nfo mutants after the same treatment show only decrease in the levels of chromosomal fragmentation consistent with some linear DNA degradation.
C. Quantification of the disappearance of catastrophic chromosomal fragmentation in WT cells induced by 5-minute CN + H2O2 treatment upon their removal, compared to the lack of it in recA, recG ruvABC and xthA nfo mutants (from several gels like in ‘B’).