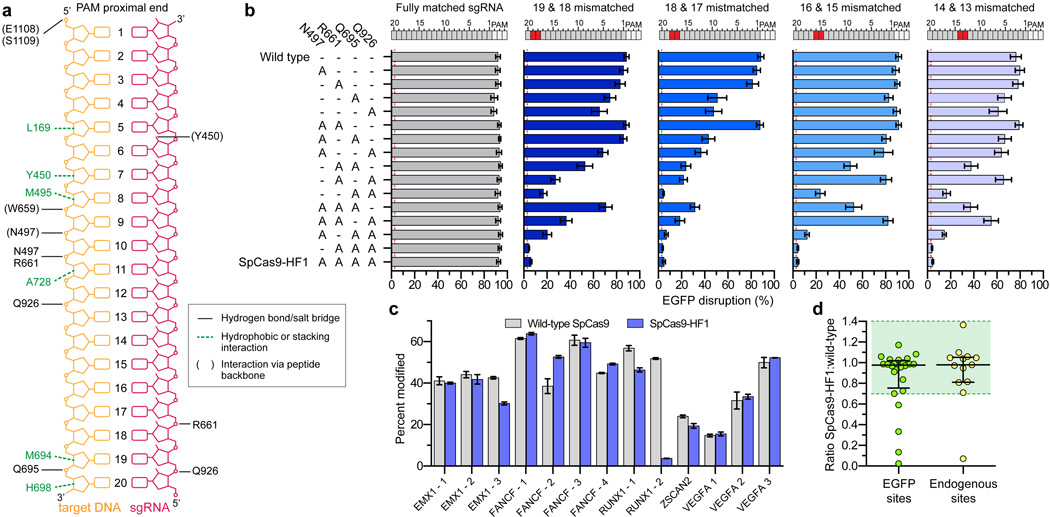
Figure 1. Identification and characterization of SpCas9 variants bearing substitutions in residues that form non-specific DNA contacts.
a, Schematic depicting wild-type SpCas9 interactions with the target DNA:sgRNA duplex, based on PDB 4OO8 and 4UN3 (adapted from refs. 28 and 29, respectively). b, Characterization of SpCas9 variants that contain alanine substitutions in positions that form hydrogen bonds with the DNA backbone. Wild-type SpCas9 and variants were assessed using the human cell EGFP disruption assay when programmed with a perfectly matched sgRNA or partially mismatched sgRNAs. Error bars represent s.e.m. for n = 3; mean level of background EGFP loss represented by red dashed line. c, On-target activities of wild-type SpCas9 and SpCas9-HF1 across 13 endogenous sites measured by T7E1 assay. Error bars represent s.e.m. for n = 3. d, Ratio of on-target activity of SpCas9-HF1 to wild-type SpCas9. The median and interquartile range are shown; the interval with >70% of wild-type activity is highlighted in green.