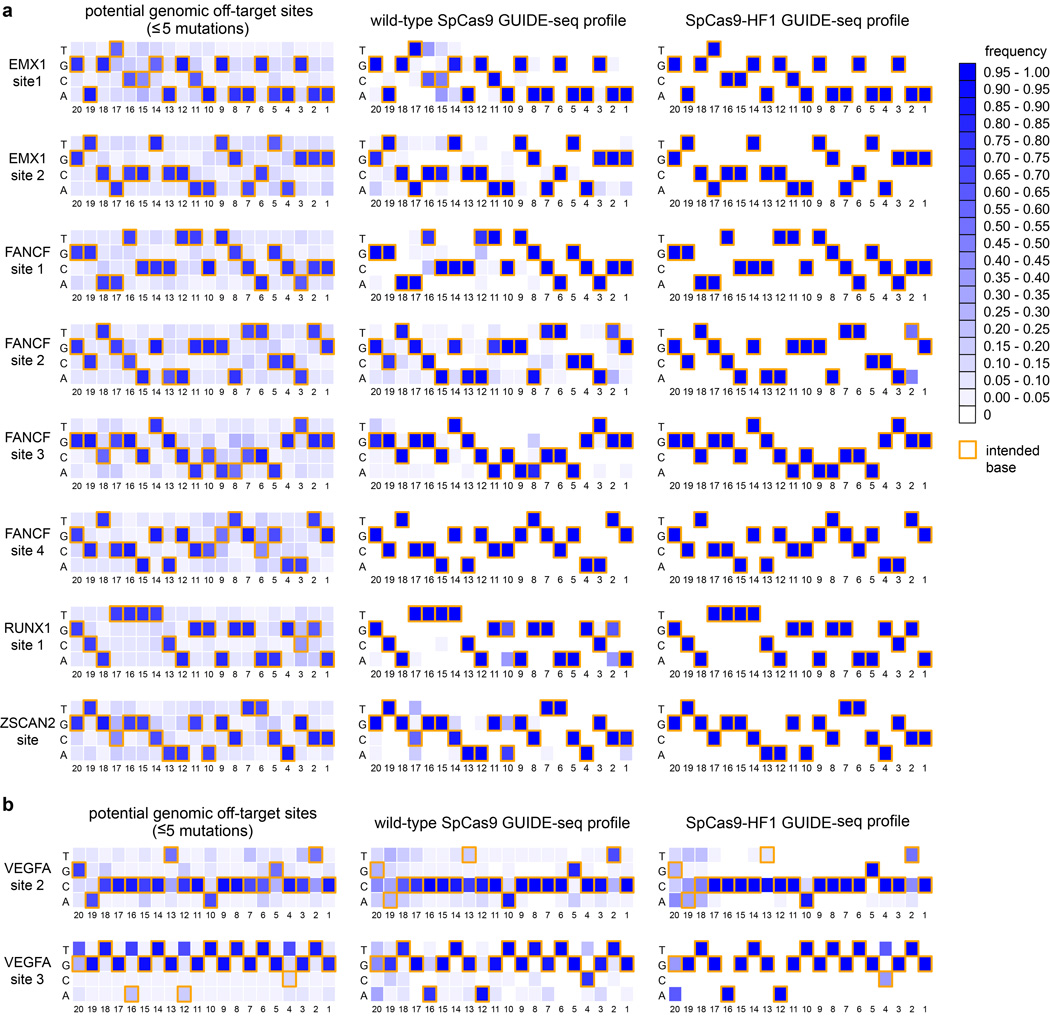
Extended Data Figure 4. Positional summary of off-target sites identified by GUIDE-seq.
Heat maps derived from GUIDE-seq data with sgRNAs targeting a, non-repetitive, or b, repetitive or homopolymeric sites in the genome are shown. Base frequencies in the set of all potential genomic off-target sites (weighted equally) with NGG PAMs and five or fewer mutations for each sgRNA are shown on the left. Summaries of off-target sites identified by GUIDE-seq for wild-type SpCas9 and SpCas9-HF1 (both weighted by read count) are shown on the right. Yellow box outlines denote on-target bases at each position. Positions (20-1) are shown below the heat maps, with 1 being the most PAM-proximal position. Note the presence of mismatches that would be expected to create potential wobble interactions (G→A or T→C) at certain positions among the off-target sites induced by wild-type SpCas9 and that SpCas9-HF1 appears to improve off-target sites without any obvious positional bias.