Figure 4.
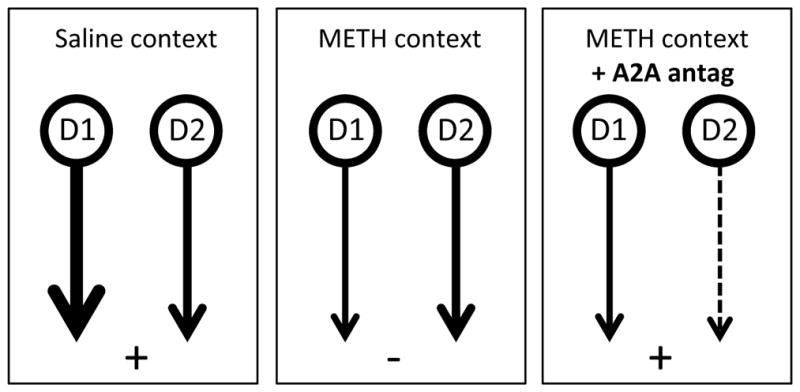
Illustration of hypothetical activity in the D1 and D2 output pathways from DMS during the negative feedback tests in the current study. When tested in the saline context (left panel) activation of the D1 neurons coincides with goal-directed performance, whereas in the METH paired context (center panel), a reduction in activity in D1 neurons results in a relative increase in activation of the D2 pathway and habitual performance. Administration of the A2A antagonist (right panel) is predicted to reduce activity in the D2 pathway, and to result in a relative increase in activity in the D1 pathway. By rebalancing the relative output of the D1 and D2 pathways this treatment is hypothesised to restore goal-directed action.
