Fig. 5. Locally evoked brainstem SD triggers cortical suppression and cardiorespiratory collapse.
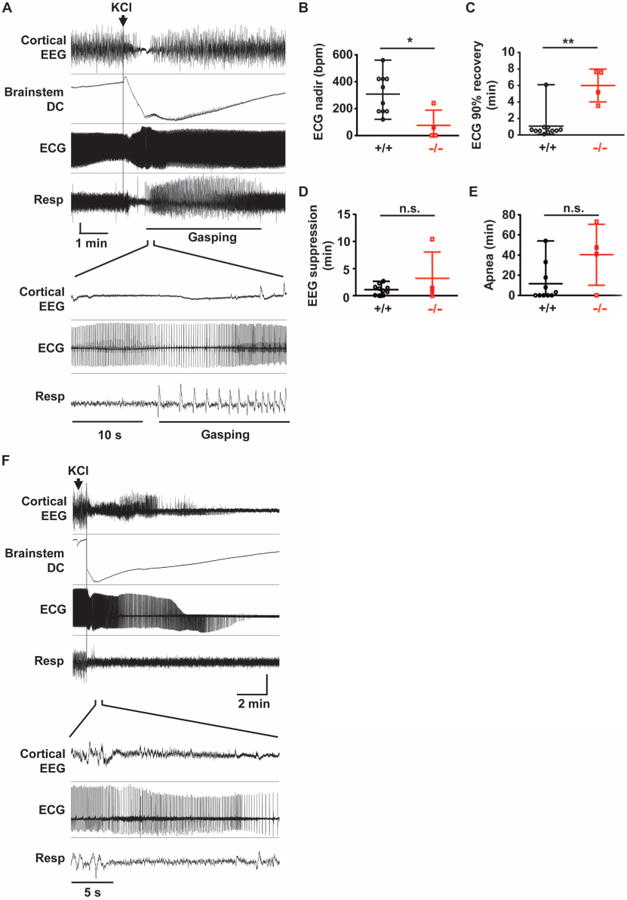
Local brainstem SD initiated by KCl microinjection into the dorsal medulla of anesthetized spontaneously breathing mouse. (A) Representative cortical and cardiorespiratory responses in juvenile WT mouse. Brainstem SD transiently suppressed cortical EEG, ECG, and spontaneous respiration. The expanded trace shown below illustrates periodic cortical EEG suppression, bradycardia, and apnea. Gasping was observed during the recovery from apnea. Vertical scale: cortical EEG, 0.15 mV; brainstem DC, 4.5 mV; ECG, 0.2 mV; respiration, arbitrary unit. (B to E) Quantification of central and peripheral consequences of brainstem SD. Duration of bradycardia was longer and the peak heart rate decrease (analyzed every 1-s bin) was lower in Kv1.1 KO mice. There was no difference in the duration of cortical EEG suppression and the duration of apnea. WT, n = 10; Kv1.1 KO, n = 4. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01; n.s., not significant. We note that 63% (7 of 11) of Kv1.1 KO mice died after SD and were excluded from the analyses. (F) Microinjection of KCl triggered prolonged DC potential shift, followed by death. Vertical scale: cortical EEG, 0.25 mV; brainstem DC, 10 mV; ECG, 0.18 mV; respiration, arbitrary unit.
