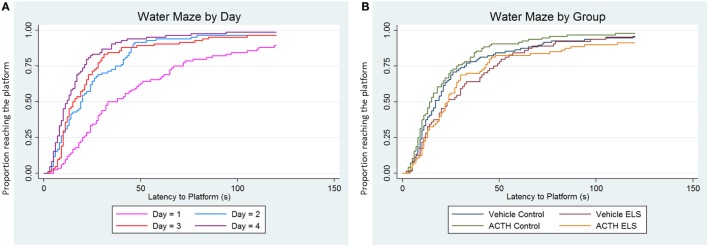
Figure 2.
ELS-associated deficits in water maze are not improved with ACTH. Time-to-event (survival) analysis of the latency to find the platform in a Morris water maze task show that animals have a shorter latency to find the platform on day 4 (purple line) compared to day 1 (pink line). This indicates that, when adjusted for group, animals on average learn over the 4-day time course of the experiment (A). We then show in (B) that animals with a history of ELS have significant deficits in water maze (green line) over controls (blue line), seen as an increased proportion of animals having longer latencies to find the platform when day and trial are accounted for statistically. Treatment with ACTH during the time of the seizures does not improve this deficit (yellow line). Likewise, treatment with ACTH does not alter latency to find the platform in control animals (red line) as well.