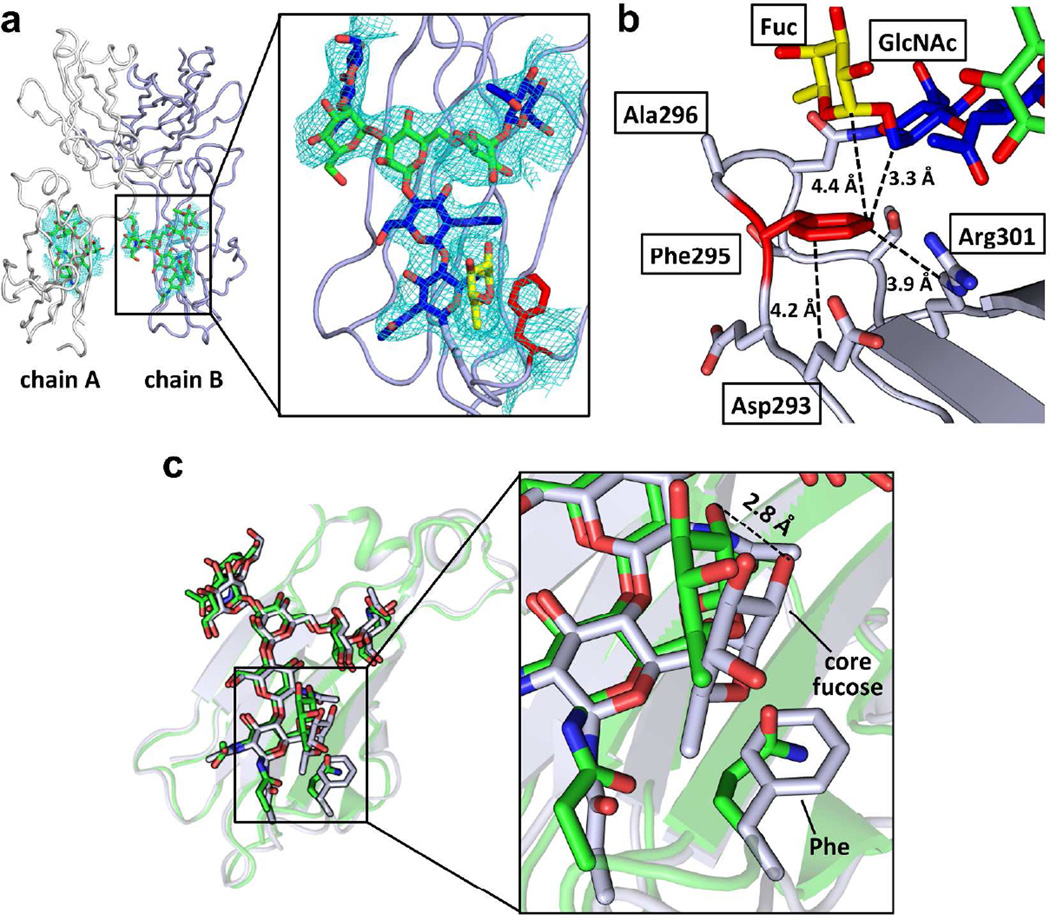
Figure 3. Crystal structure of the Fc variant FA.
(a) Overview (left) of the crystal structure of Fc variant FA (PDBID:4QGT) and a close-up view of the N-glycan and the engineered region of chain B of the CH2 domain (right). The protein part of Fc is shown in ribbon format (chain A colored in white and chain B colored in light purple) and N-glycans are depicted in stick format. In the close-up view, the GlcNAc of the N-glycan is colored in blue, the mannose in green and the core fucose in yellow. The GlcNAc1 and the core fucose are interacting with the engineered Phe (red) in the Fc. The 2Fo-Fc map contoured at 1 sigma for the N-glycan and Phe is shown. (b) The engineered Phe residue packs with the aliphatic portion of the side chains of Asp293 and Arg301 and with GlcNAc1 and the core fucose of the N-glycan. Distances are shown in Å. (c) Alignment of the CH2 domains of the wild type (3AVE, green) and EAS-stabilized (grey) FA variant Fc chain B structures. The N-glycan and the side chain of Gln295 in the wild-type and the Phe295 in the EAS-stabilized Fc structures are shown in stick format. The N-glycans of the wild type Fc and the EAS-stabilized Fc align very well, with the largest difference being the orientation of the core fucose. In the EAS-stabilized Fc, this fucose is shifted closer to the engineered Phe295 residue by about 2 Å (see inset).