Figure 5.
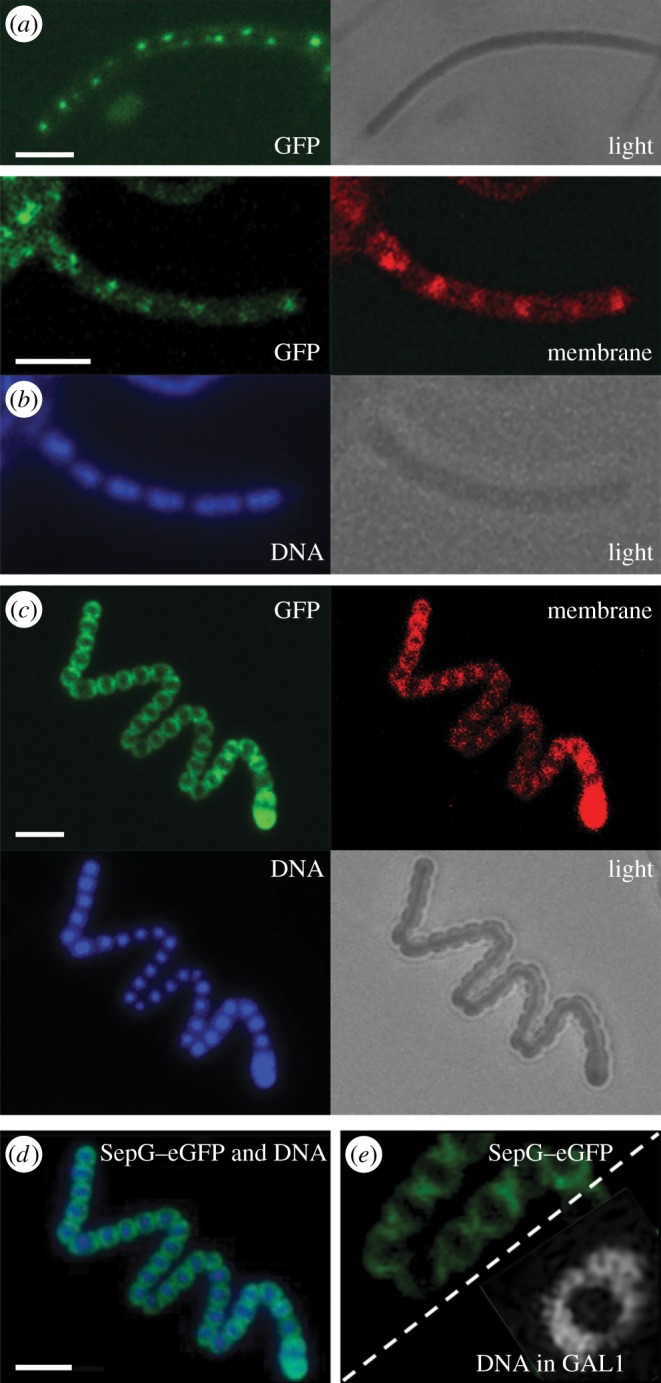
Localization of SepG in S. coelicolor. (a–c) Sporogenic aerial hyphae of S. coelicolor M145 were imaged by fluorescence microscopy visualizing SepG–eGFP, membrane (stained with FM5–95), DNA (stained with DAPI) and a light micrograph at the onset of sporulation in aerial hyphae (a), during sporulation (b) and spore maturation (c). (d) A merged image of SepG–eGFP and the DNA taken from (c). (e) SepG–eGFP in wild-type cells (strain GAL7; left) showing a similar localization in the spores as the DNA in the sepG null mutant (strain GAL93; right), suggesting that SepG aids in DNA condensation in the centre of the spores. Note that the images in panel (e) are only presented for comparison, as the sepG–GFP data were obtained from panel (d) (FM imaging), while the nucleoid was obtained from figure 4a (STED imaging). Scale bar, 3 µm.
