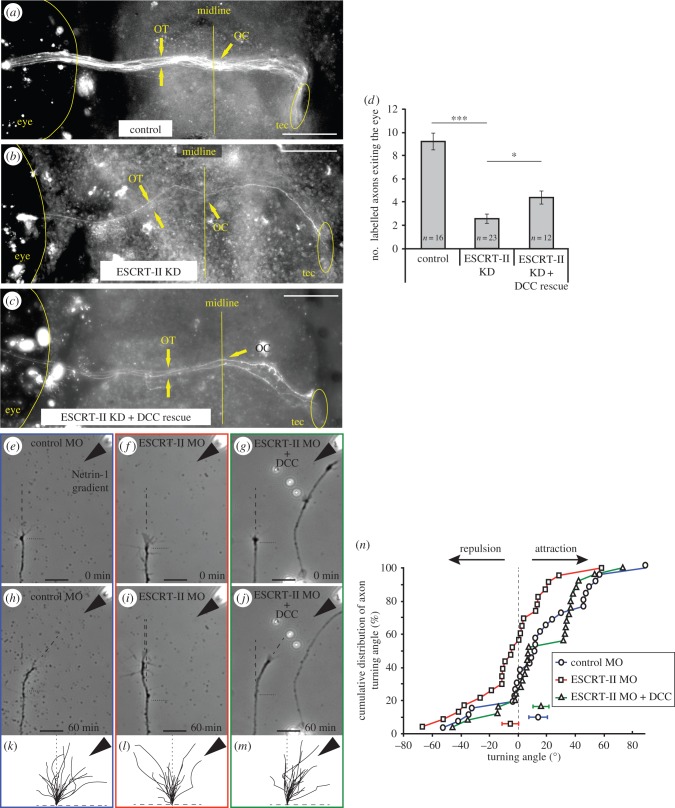
Figure 8.
DCC rescues ESCRT-II knockdown phenotypes. (a–d) In vivo ventral view of the Xenopus optic path in stage 41 embryos whose right eye had been electroporated with control MO (a), ESCRT-II MO (b) and ESCRT-II MO + DCC mRNA (c). The numbers of axons exiting the eye and navigating in the optic pathway were counted and the quantification is shown in (d). OT, optic tract; OC, optic chiasm; tec, optic tectum. (e–o) In vitro turning assay. (e–j) Representative examples of RGC axons from embryos injected with control MO (e,h), ESCRT-II MO (f,i) and ESCRT-II MO + DCC mRNA (g,j) before (e–g) and after (h–j) being subjected to a Netrin-1 gradient ejected from a pipette (indicated with black arrowheads) set at 45° angle from the direction of growth. Growth measurement start point is indicated with horizontal black dotted line; dashed lines show the measured directions of growth at time 0 min and 45 min. (k–m) Traces of control (k), ESCRT-II MO (l) and ESCRT-II MO + DCC mRNA (m) axons growing for 1 h while exposed to Netrin-1 gradient (black arrowheads). (n) Cumulative distribution plot showing the turning angles of all measured axons. *p ≤ 0.05, ANOVA + uncorrected LSD Fisher's test. Scale bars, 20 µm.