Figure 1.
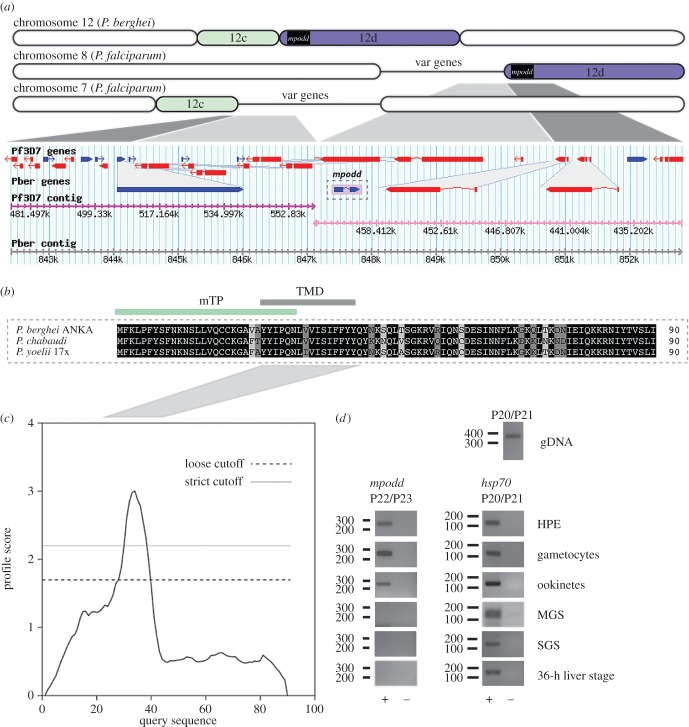
mpodd codes for a transmembrane protein and is located on a synteny break between rodent and human malaria species. (a) Organization of P. berghei chromosome 12 in comparison to chromosomes 7 and 8 from P. falciparum strain 3D7 (not drawn to scale). Evolutionary chromosome rearrangements have resulted in fragmentation of chromosome 12. Therefore, the equivalent segment of P. berghei 12d localizes to chromosome 8 in P. falciparum while segment 12c localizes on chromosome 7. As indicated, mpodd is the first protein coding gene on segment 12d. Sites of crossing-over events are marked by congregations of var genes. Gene locus of mpodd retrieved from PlasmoDB is shown below the scheme: genes are indicated as blue and red arrows, breaks within arrows indicate introns. Corresponding contigs are indicated below the genes. (b) Multiple sequence alignment of MPODD from P. berghei ANKA with its homologues in P. chabaudi, and P. yoelii 17X. Conserved residues are written in white and highlighted in black, highly conserved residues are highlighted in dark grey and mostly conserved residues are highlighted in light grey. Predictions (§2.1) indicate the presence of a transmembrane domain (TMD) and a mitochondrial targeting peptide (mTP) shown as green and black line above the alignment. The alignment was performed with the multiple sequence alignment tool Clustal Omega (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/clustalo/). (c) Hydrophobicity plot (dense alignment surface method) based on the sequence of Pb MPODD indicates the presence of a transmembrane domain between tyrosine 25 and tyrosine 40. (d) Total RNA was isolated from indicated life cycle and used in RT-PCR with mpodd-specific primers; (+) and (−) indicate RT+ and RT− cDNA synthesis reactions. Primers specific for hsp70 were used as an expression control for all stages. Amplification of genomic DNA (gDNA) shows the presence of an intron. HPE, non-gametocyte producer line/asexual stage parasites. MGS, midgut sporozoites. SGS, salivary gland sporozoites.