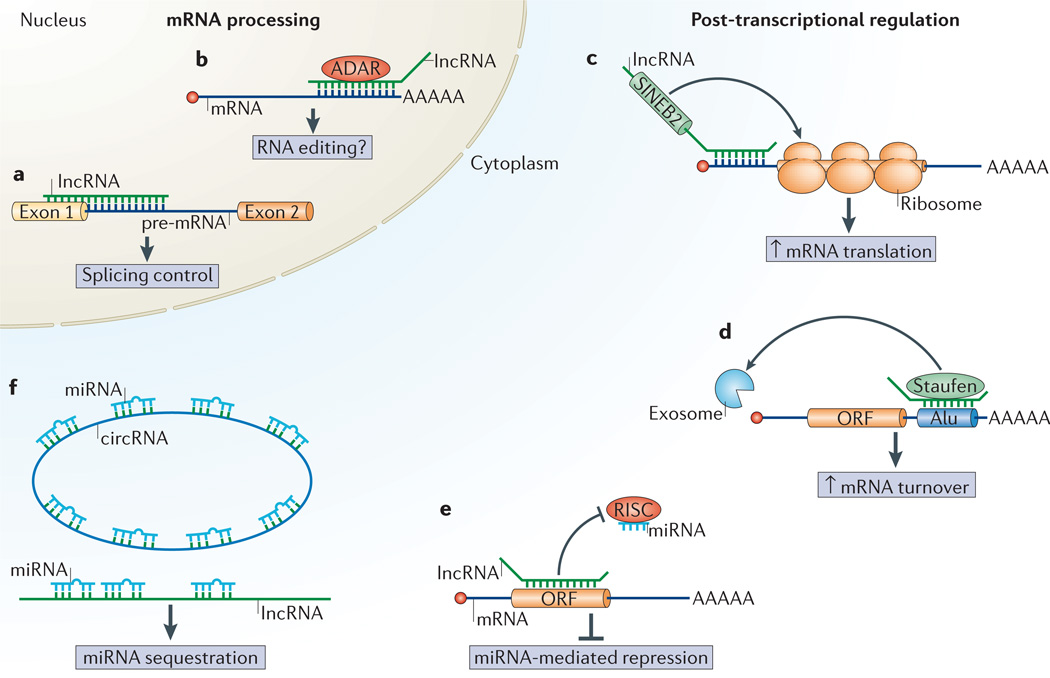
Figure 3. lncRNAs influence mRNA processing and post-transcriptional regulation.
a,b | Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) can modulate mRNA processing. Splicing patterns can be influenced by lncRNAs that associate with the pre-mRNA(part a). For example, splicing of the first intron of neuroblastoma MYC mRNA is prevented by a natural antisense transcript61. Antisense lncRNAs that associate with an mRNA could direct mRNA editing, perhaps through association of the duplex with ADAR (adenosine deaminase acting on RNA) enzymes that catalyse adenosine to inosine conversion in double-stranded RNA63,66 (part b). c-f | lncRNAs modulate post-transcriptional regulatory events. lncRNAs containing SIN EB2 repeat elements can upregulate translation through association with the 5′ region of an mRNA68 (part c). lncRNAs containing Alu repeat elements associate with the Alu elements in the 3′ untranslated region (UTR)of an mRNA, and this double-stranded structure can direct Staufen-mediated decaythrough a pathwaythat is molecularly similar to nonsense-mediated decay70 (part d). lncRNAs can mask miRNA-binding sites on a target mRNA to block miRNA-induced silencing through the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC)72 (part e). Linear or circular lncRNAs can function as miRNA decoys to sequester miRNAs from their target mRNAs74,75 (part f).