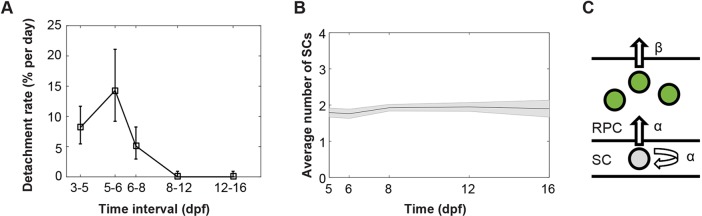
Fig. 3.
Stabilization of CMZ clones is due to asymmetrical RSC division. (A) The rate of clone detachment events plotted as a function of age. Detachment rate is defined as the number of detachment cases (clones move away from rings 1-2 in a specific period of time) divided by the total number of cases surviving up to that time point, divided by the number of days in the time period. (B) Plot showing the average number of ring 1+ring 2 cells in the maintained clones as a function of age. Note that this number remains relatively constant in the maintained clones, indicating potential asymmetrical division of RSCs. (C) Model of RSC and RPC division, with α and β indicating the division rate of RSCs and RPCs, respectively.