Fig. 1.
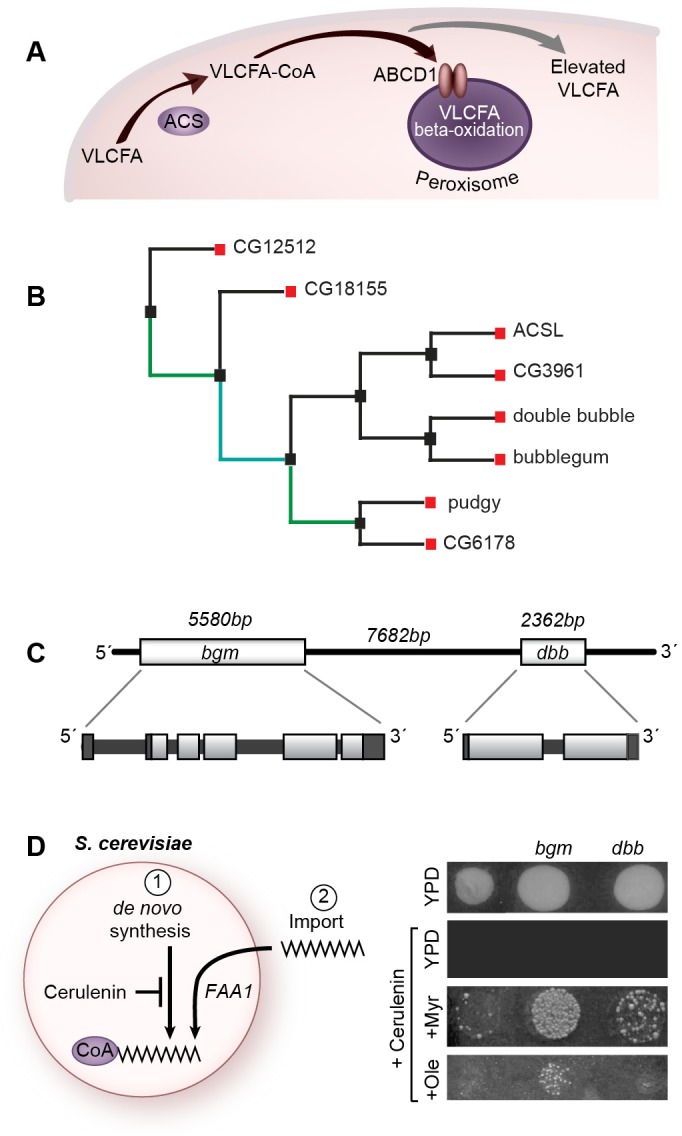
bgm and dbb are duplicated genes that encode bona fide acyl-CoA synthetases. (A) Enzymology of VLCFA degradation in peroxisomes. When transport to the peroxisome is blocked by mutation of either the synthetase (ACSL) or the transporter (ABCD1), which is shown here as a dimer (oval pair) resident in the peroxisomal membrane, VLCFAs accumulate intracellularly (gray arrow). (B) A phylogenetic tree of all annotated mono-functioning acyl-CoA synthetase proteins in D. melanogaster. The tree was made using the software PhylOgenetic Web Repeater (POWER) by aligning amino acid sequences. Standard conditions were used, with the exception of the following: no outgroup was applied and bootstrapping was used to determine the best-fit tree. Colors indicate the number of times that line was established out of 100 assembled phylogenetic trees (bootstrapping). Teal indicates between 40-60 times, and green indicates between 60-80 times. (C) Organization of the bubblegum (bgm) and double bubble (dbb) genes on Drosophila chromosome 2. (D) Cerulenin renders yeast auxotrophic and dependent on imported fatty acids and the activity of FAA1. Both bgm and dbb restore growth to FAA1-deficient yeast when myristate is added to the growth medium. Only bgm complements FAA1 in the presence of oleate. YPD, yeast peptone dextrose.
