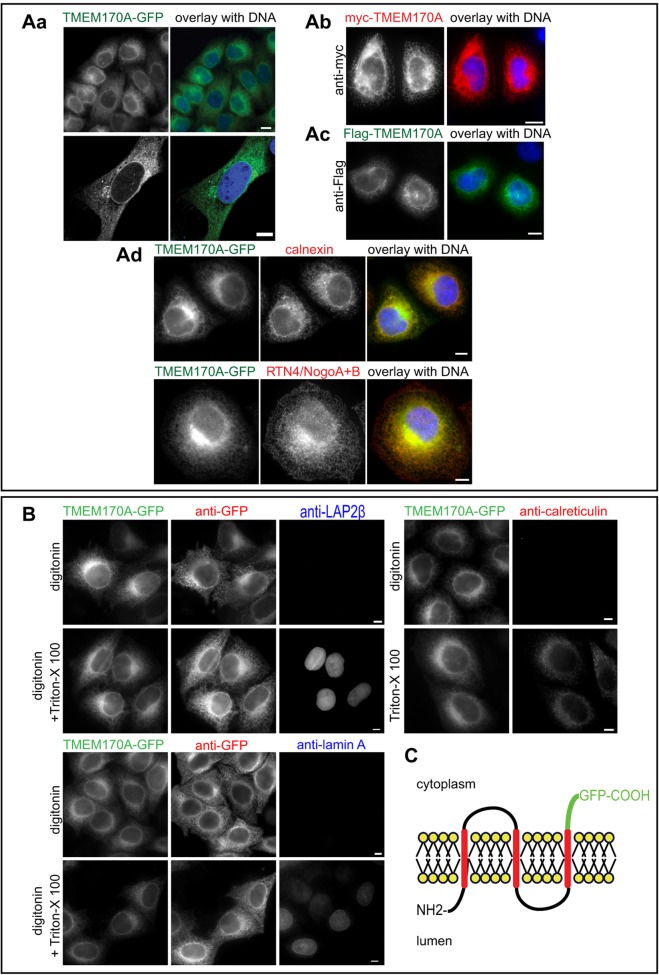
Fig. 1.
Localization and membrane topology of human TMEM170A. (A) TMEM170A localizes to the nuclear envelope and the ER. (Aa–c) Immunofluorescence of HeLa K cells transiently transfected with TMEM170A–GFP (green), FLAG–TMEM170A (green) or myc–TMEM170A (red). DNA was visualized with Hoechst in all panels (blue). (Ad) Immunofluorescence of HeLa K cells transiently transfected with TMEM170A–GFP (green) and co-stained for ER markers calnexin (red) or RTN4/NogoA+B (red). (B) The C-terminal domain of TMEM170A faces the cytoplasm. HeLa K cells, stably expressing TMEM170A–GFP, were fixed and subjected to 0.05% w/v digitonin to permeabilize the plasma membrane or 0.05% w/v digitonin+0.5% v/v Triton X-100 to permeabilize both the plasma membrane and the nuclear envelope. Cells were stained with anti-GFP antibody (green) in combination with either anti-LAP2β or anti-lamin-A or calreticulin (red). TMEM170A–GFP is accessible to the anti-GFP antibody in digitonin-only semi-permeabilized cells, whereas LAP2β, lamin A and calreticulin are only recognized upon full permeabilization. (C) Schematic of the membrane topology of TMEM170A. Transmembrane segments were predicted with TMPRED and topology of the C-terminus was confirmed in the experiments shown in B that support the model shown. Scale bars: 10 μm.