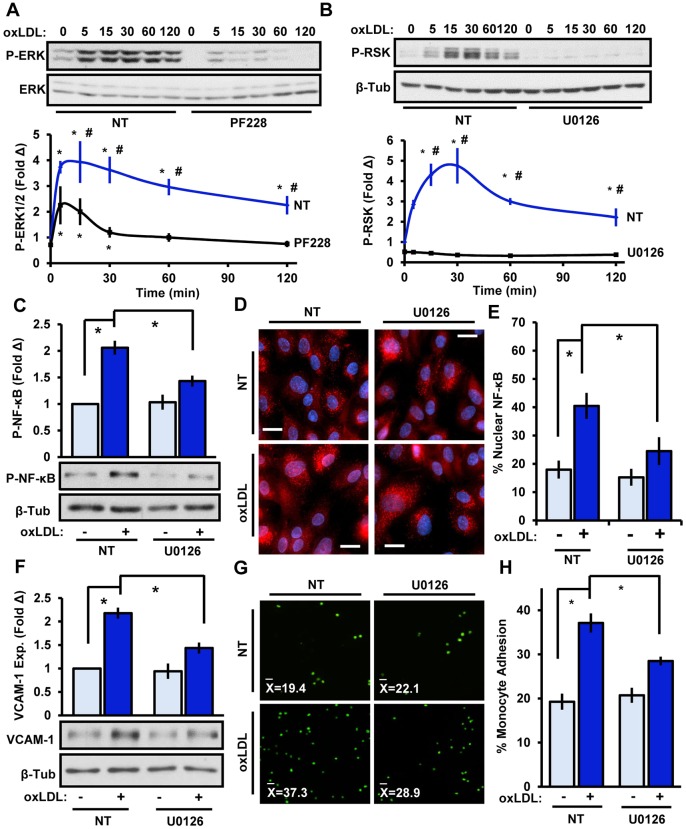
Fig. 4.
FAK-dependent ERK1/2 signaling mediates RSK activation and proinflammatory signaling. (A) oxLDL-induced (100 μg/ml, indicated times) ERK activation was assessed in HAECs following treatment with the FAK inhibitor PF-573228 (PF228, 4 μM, 1 h). (B) ERK signaling in endothelial cells was reduced by pretreatment with the MEK1/2 inhibitor U0126 (10 μM, 1 h), and oxLDL-induced RSK signaling was assessed by immunoblotting (n=5). (C–H) Endothelial ERK1/2 signaling was reduced by using U0126, and oxLDL-induced (C) NF-κB phosphorylation (P-NF-κB, 1 h, n=5), (D,E) p65 nuclear localization (1 h, n=4), (F) VCAM-1 expression (exp., 6 h, n=4) and (G,H) monocyte adhesion (6 h, n=4) were assessed. Results are mean±s.e.m. *P<0.05 (compared to 0 time or no treatment) or #P<0.05 (compared to respective timepoint) using two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-hoc test. NT, no treatment.