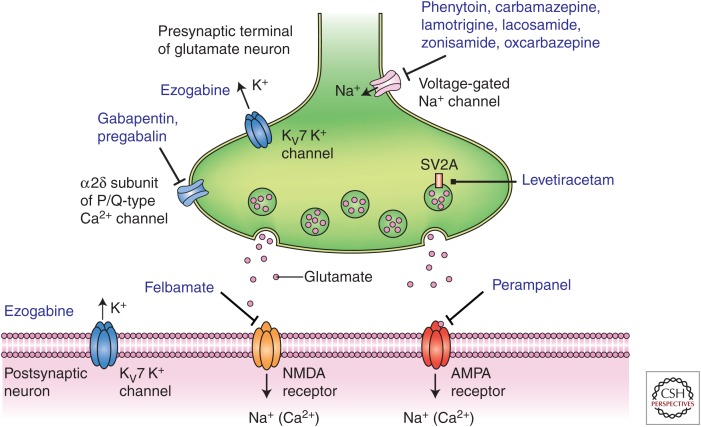
Figure 1.
Diverse molecular targets for antiseizure drugs (ASDs) at excitatory glutamatergic synapses. Seizure protection can be conferred by effects on voltage-gated sodium channels, M-type voltage-gated potassium channels (Kv7), and voltage-gated calcium channels located in presynaptic terminals. Additional presynaptic targets include the synaptic vesicle protein SV2A and the α2δ accessory subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels. These presynaptic targets may act to diminish glutamate release. Postsynaptic targets include ionotropic glutamate receptors of the N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) and α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole-propionate (AMPA) types.