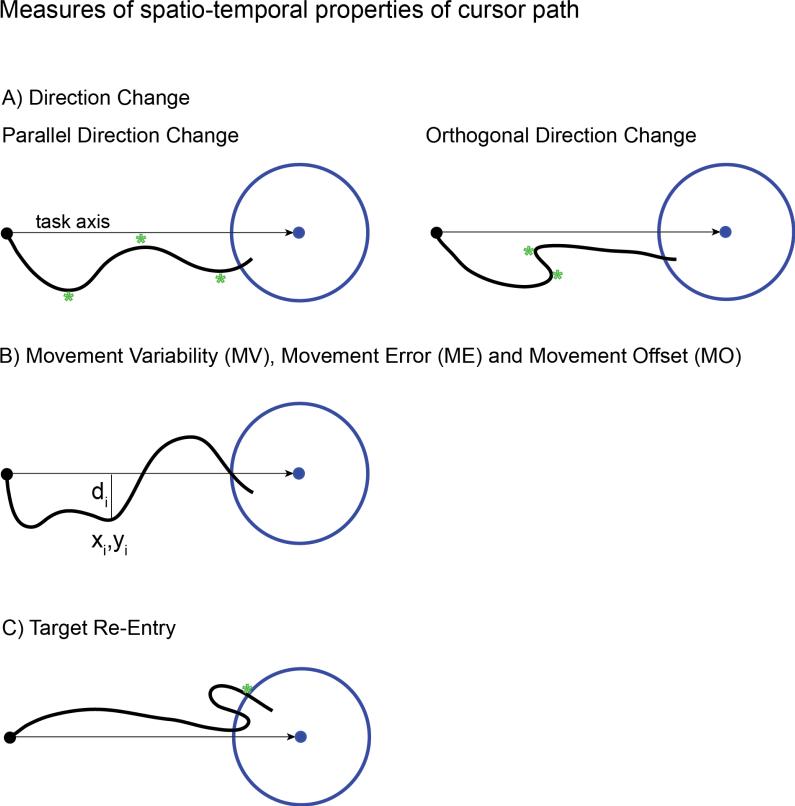
Figure 2.
Illustration of cursor path measures that capture spatio-temporal characteristics of the dual control task. (A) Direction change counts the number of times the cursor changes direction parallel (left) and orthogonal (right) to the task axis (the straight line connecting the cursor and target when the target appears). Direction changes are indicated by a green star. (B) Movement Variability, Movement Error and Movement Offset are calculated by summing the orthogonal distance from each sample point to the task axis as the cursor approaches the target (see equations (1)-(3) in methods). (C) Target re-entry counts the number of times the cursor re-enters the target after the initial entry, marked by a green star in this example.