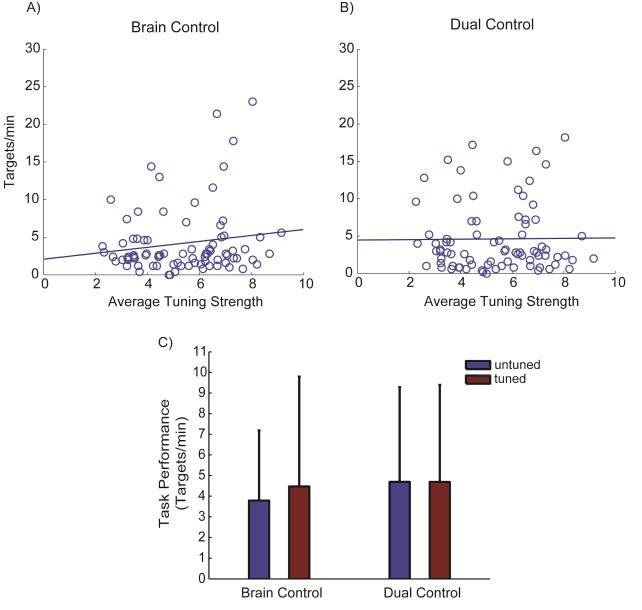
Figure 3.
Task performance relative to unit directional tuning. Regression of tuning strength measured during wrist tracking versus the number of targets per minute acquired during peak performance for (A) brain control and (B) dual control task. Regressions of performance across tuning strength of the units controlling the task were not significant for either task (R2 ≤ 0.02, p ≥ 0.18). (C) The average number of targets per minute acquired by untuned and tuned units during peak performance of each task. The monkey performed both tasks equally well using the untuned and tuned cells during brain control (p = 0.906) as well as during dual control tasks (p = 0.972). Values in (C) are mean + SD.