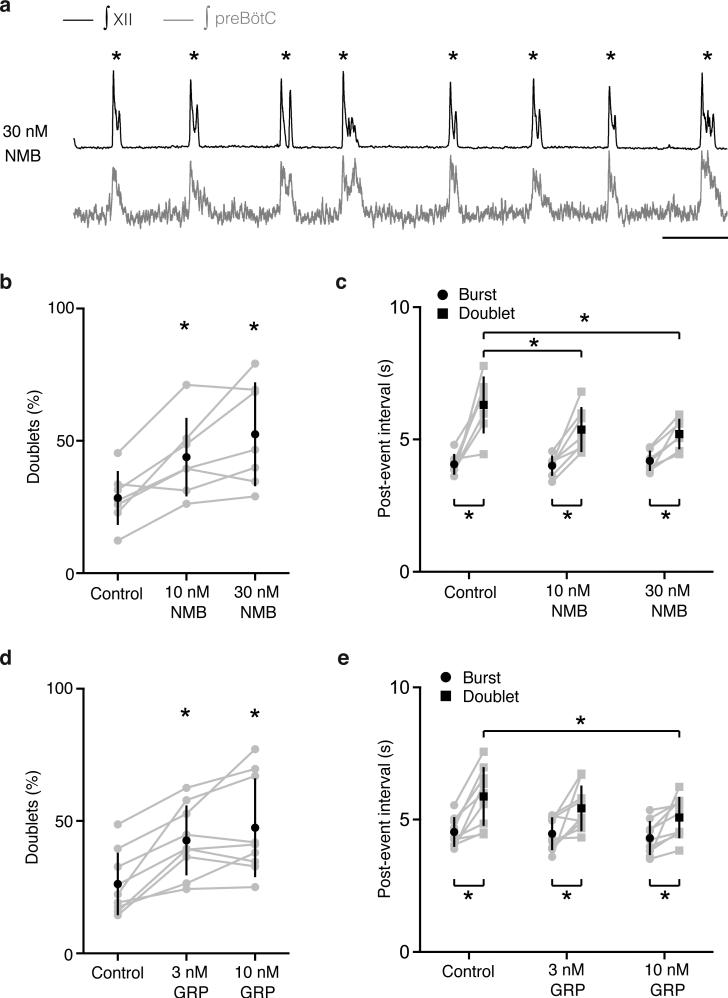
Extended Data Figure 5. Effect of NMB on rhythmic activity of preBötC slice.
a, Neuronal activity trace (∫XII, black; ∫preBötC population activity, grey) of preBötC slice containing 30 nM NMB, as in Figure 2e. Note the extreme effect of NMB in which every burst (“breath”) in the trace is a doublet (“sigh”, *). Bar, 5 s. b,c, NMB increases the doublet rate by increasing the fraction of total events that are doublets (b) and decreasing the interval following a doublet (c). *, p<0.05, n=7. d,e, GRP also increases the doublet rate by increasing the fraction of total events that are doublets (d) and decreasing the interval following a doublet (e). *, p<0.05, n=9. Note that post-doublet intervals are significantly longer than post-burst intervals under all conditions, consistent with longer post-sigh apneas in vivo.