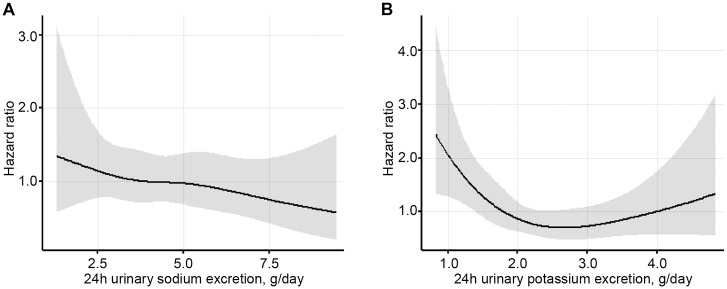
Fig 2. Association between 24h (A) urinary sodium and (B) potassium excretion and hazard ratio for 30% decline in eGFR or death.
Multivariable spline regression analyses of hazard ratios and 95% confidence intervals of 30% decline of eGFR or death, adjusted for age, sex, body mass index, history of CVD, diabetic retinopathy, blood pressure, HbA1c, eGFR, uric acid, total cholesterol, high density lipoprotein, 24h urinary albumin excretion and (A) 24h urinary potassium excretion or (B) 24 urinary sodium excretion.