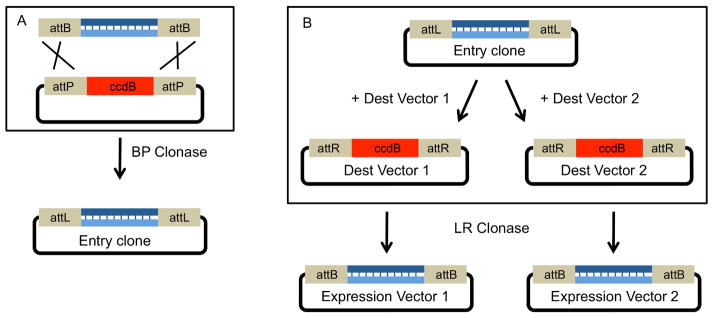
Figure 2. Single segment cloning using Gateway.
A. Single segment Gateway cloning. An attB-flanked, blunt-ended PCR product is recombined with an attP containing plasmid. The acceptor plasmid expresses the positive selection marker ccdB, a bacterial toxin that targets DNA gyrase (Bernard et al., 1994), so that only plasmids that have replaced this gene with the insert can replicate without killing their host. After a successful recombination facilitated by int and IHF (BP Clonase), the ccdB gene is replaced by the insert segment. The final plasmid carries the insert flanked by attL sites and is known as an Entry clone.
B. The insert from an Entry clone can be subcloned into multiple Destination vectors. In this example, the insert from the same Entry clone is subcloned into two distinct Destination vectors via an LR clonase reaction. Again, the ccdB positive selection marker is used. This flexibility allows a researcher to easily create many unique expression vectors from the same Entry clone.