Figure 4.
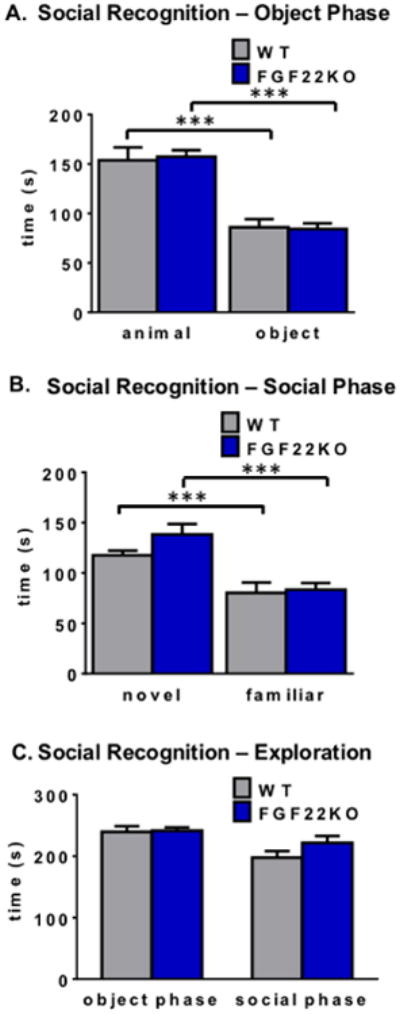
FGF22KO mice display normal learning and memory in a social cognitive task. A. In a standard social preference task, WT and FGF22KO animals prefer a novel animal over an object (two-way ANOVA, main effect of test object, F1,66=71.21, p<0.0001; ***Tukey's HSD p<0.001; main effect of genotype, F1,66=0.013, p=0.91; interaction effect, F1,66=0.096, p=0.76). B. In the social recognition stage of the task, WT and FGF22KO animals prefer a novel animal over a familiar one (two-way ANOVA, main effect of test animal, F1,66=21.63, p<0.0001; ***Tukey's HSD p<0.001; main effect of genotype, F1,66=1.45, p=0.23; interaction effect, F1,66=0.79, p=0.38). C. FGF22KO mice spend a similar amount of time exploring stimuli during the object phase as WT littermates (Student's unpaired two-tailed t-test, t(33)=0.19, p=0.85). Both FGF22KO and WT mice also explore stimuli during the social phase to a similar extent (Student's unpaired two-tailed t-test, t(33)=1.31, p=0.20).
