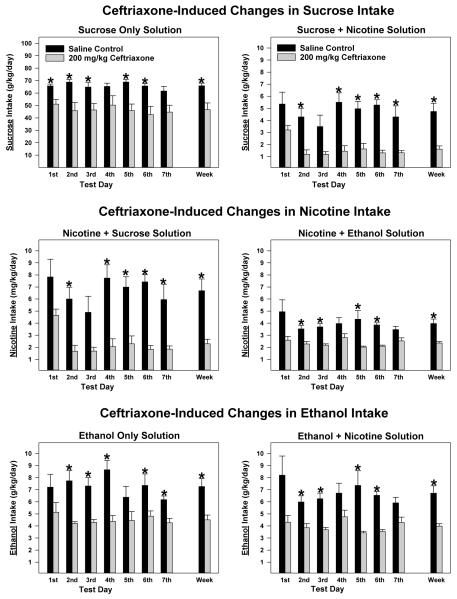
Figure 1.
The effects of 7 consecutive daily ceftriaxone (200 mg/kg, n = 5/treatment by test solution group) and saline (n = 5/treatment by test solution group) injections on average (± S.E.M.) intake of multiple test solutions by adult female alcohol-preferring P rats. Sucrose (g/kg/day) intakes by animals receiving the sucrose only test solution (5% and 10% available concurrently) are displayed in the left top panel; and sucrose intakes by animals receiving the sucrose + nicotine test solution (5% sucrose + 0.07 mg/ml nicotine and 10% sucrose + 0.14 mg/ml nicotine available concurrently) are displayed in the right top panel. Nicotine (mg/kg/day) intakes by animals receiving the nicotine + sucrose test solution (5% sucrose + 0.07 mg/ml nicotine and 10% sucrose + 0.14 mg/ml nicotine available concurrently) are displayed in the left middle panel; and nicotine intakes by animals receiving the nicotine + ethanol test solution (15% ethanol + 0.07 mg/ml nicotine and 30% ethanol + 0.14 mg/ml nicotine available concurrently) are displayed in the right middle panel. Ethanol (g/kg/day) intakes by animals receiving the ethanol only test solution (15% and 30% available concurrently) are displayed in the left bottom panel; and ethanol intakes by animals receiving the ethanol + nicotine test solution (15% ethanol + 0.07 mg/ml nicotine and 30% ethanol + 0.14 mg/ml nicotine available concurrently) are displayed in the right bottom panel. Within these panels test solution intake for each treatment day, the average across the 7 days of treatment and the 7 day average converted to percent relative to the saline group are displayed. *, indicates a significant (p < 0.025) difference between the ceftriaxone- and saline-treated animals. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.