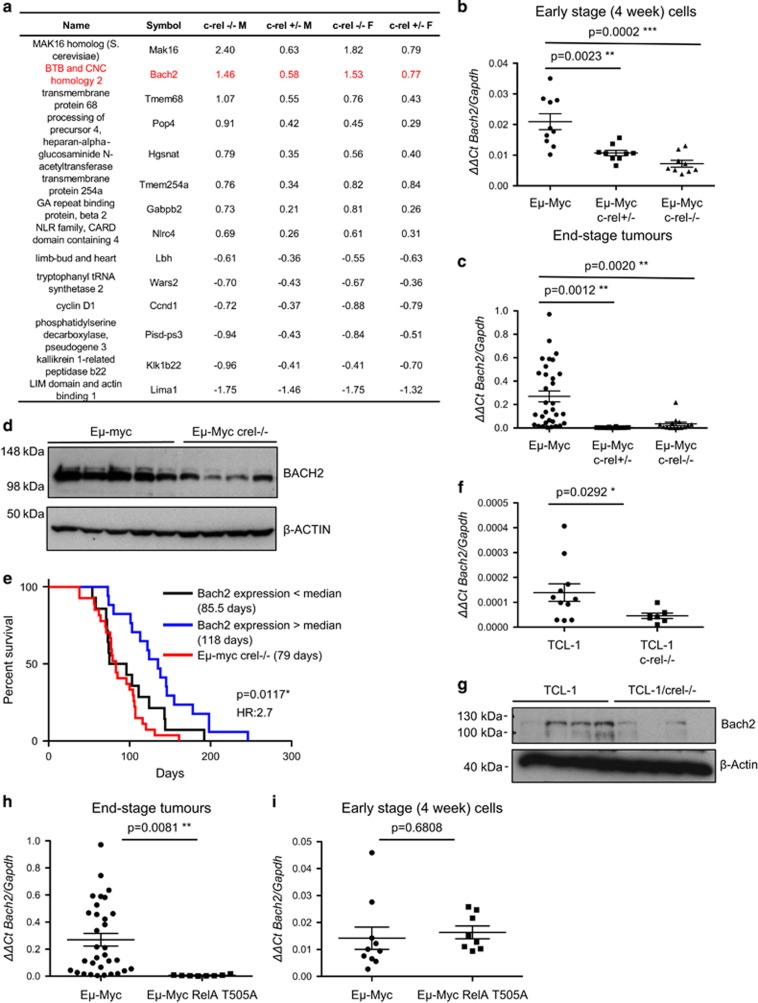
Figure 3.
Expression of the B-cell tumour suppressor Bach2 is dependent on c-Rel in Eμ-Myc lymphoma. (a) Table showing genes whose expression is regulated by c-Rel from microarray analysis of bone marrow-derived B cells from 4-week-old Eμ-Myc, Eμ-Myc/c-rel+/– and Eμ-Myc/c-rel–/– mice. Fold changes shown are compared with equivalent wild-type cells and are in log2 (a positive number indicates higher expression in wild-type cells). Bone marrow-derived B cells were purified from 4-week-old Eμ-Myc or Eμ-Myc/c-rel+/–, Eμ-Myc/c-rel+/– mice using CD19 microbeads (MACS Miltenyi Biotec, Surrey, UK). Total B-cell RNA, purified using the PeqGold total RNA extraction kit (Peqlab, VWR, Lutterworth, UK), was then used for microarray analysis at Cambridge Genomic Services (University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK) using the Illumina mouse WG-6 Expression BeadChip system (San Diego, CA, USA). These data were background corrected in Illumina GenomeStudio and subsequent analysis proceeded using the lumi and limma packages in R (Bioconductor, Seattle, WA, USA).46, 47, 48 Variant stabilisation transform and robust spline normalisation were applied in lumi. Differential expression was detected using linear models and empirical Bayes statistics in limma. A list of genes for each comparison was generated using a Benjamini–Hochberg false discovery rate-corrected P-value of 0.05 as a cutoff. (b, c) Confirmation that Bach2 mRNA levels are c-Rel regulated. Quantitative-PCR (q-PCR) showing relative Bach2 expression in (b) bone marrow-derived B cells from Eμ-Myc (n=10), Eμ-Myc/c-rel+/– (n=9) and Eμ-Myc/c-rel–/– (n=9) mice and (c) end-stage tumorigenic spleens from Eμ-Myc (n=30), Eμ-Myc/c-rel+/– (n=12) and Eμ-Myc/c-rel–/– (n=11) mice. q-PCR was performed in triplicate on 20 ng cDNA (Reverse Transcriptase kit, Qiagen, Crawley, UK), using predesigned Bach2 Quanititect Primer assays (Qiagen). Samples were run and analysed on a Rotor-gene Q system (Qiagen), using murine Gapdh primers as an internal control. All cycle threshold values were normalised to Gapdh levels using the Pfaffl method.49 Data represent mean±s.e.m. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 (unpaired Student's t-test). (d) Bach2 protein levels are reduced in Eμ-Myc/c-rel–/– mice. Whole-cell extracts were prepared from Eμ-Myc or Eμ-Myc/c-rel–/– tumourigenic spleens. Cell pellets were washed with ice-cold phosphate-buffered saline, and lysed using PhosphoSafe Extraction Reagent (Merck Millipore), according to the manufacturer's protocols. Western blot analysis was performed using antibodies to BACH2 (ab83364 Abcam, Cambridge, UK) or the loading control β-ACTIN (A5441 Sigma-Aldrich). (e) Low levels of Bach2 mRNA correlate with poor survival in wild-type Eμ-Myc mice. Kaplan–Meier analysis of the survival of mice with below and above the median levels of Bach2 mRNA (from data in c). Also shown for comparison is the survival data from Eμ-Myc/c-rel–/– mice shown in Figure 1f. (f) Bach2 mRNA levels are c-Rel regulated in TCL1-Tg mice. q-PCR showing relative Bach2 expression in end-stage tumorigenic spleens from TCL1-Tg (n=11) and TCL1-Tg/c-rel–/– (n=7) mice. Data represent mean±s.e.m. *P<0.05. (g) Bach2 protein levels are reduced in TCL1/c-rel–/– mice. Whole-cell extracts were prepared from TCL1-Tg or TCL1/c-rel–/– tumourigenic spleens and western blot analysis was performed as indcated. (h, i) Low Bach2 mRNA levels in RelA T505A mice. q-PCR showing relative Bach2 expression in (h) end-stage tumorigenic spleens from Eμ-Myc (n=30) and Eμ-Myc/relaT505A (n=8) mice and (i) bone marrow-derived B cells from Eμ-Myc (n=10) and Eμ-Myc/relaT505A (n=8) mice. Note, data from wild-type Eμ-Myc mice are the same as shown in c. Data represent mean±s.e.m. **P<0.01 (unpaired Student's t-test). RelA T505A knock-in mice were generated by Taconic Artemis (Cologne, Germany) using C57Bl/6 ES cells.