Table 2.
Characteristics of and risk factors for at-risk individuals tested for hepatitis C virus at testing sites in Durham County, North Carolina, December 2012 through February 2014a
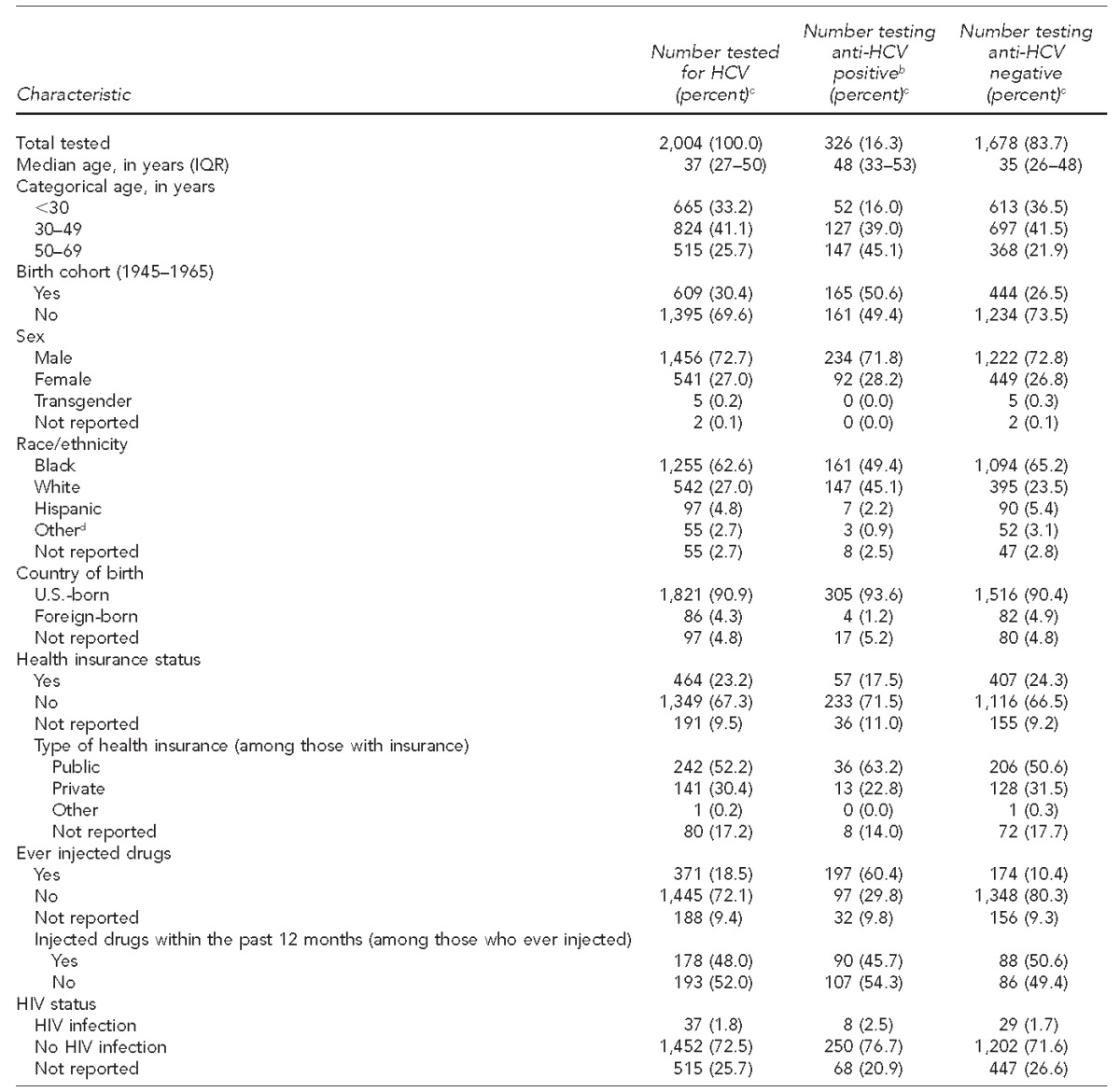
At-risk individuals included current and past injection drug users, individuals with HIV, and people born between 1945 and 1965 (i.e., baby boomers) (for one-time testing). Other risk factors included incarceration, long-term sexual exposure to an HCV-infected person, history of multiple sexual partners or sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), and men who have sex with men. Testing sites included an STD clinic, county jail, homeless health-care clinic, and community testing sites.
bThe anti-HCV-positive group included people who were anti-HCV positive/ribonucleic acid (RNA) positive or antibody positive/RNA negative.
cPercentages may not total to 100 because of rounding.
dOther race includes multiracial, Asian, American Indian/Alaska Native, and Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander.
HCV = hepatitis C virus
anti-HCV = hepatitis C virus antibody
IQR = interquartile range
HIV = human immunodeficiency virus
