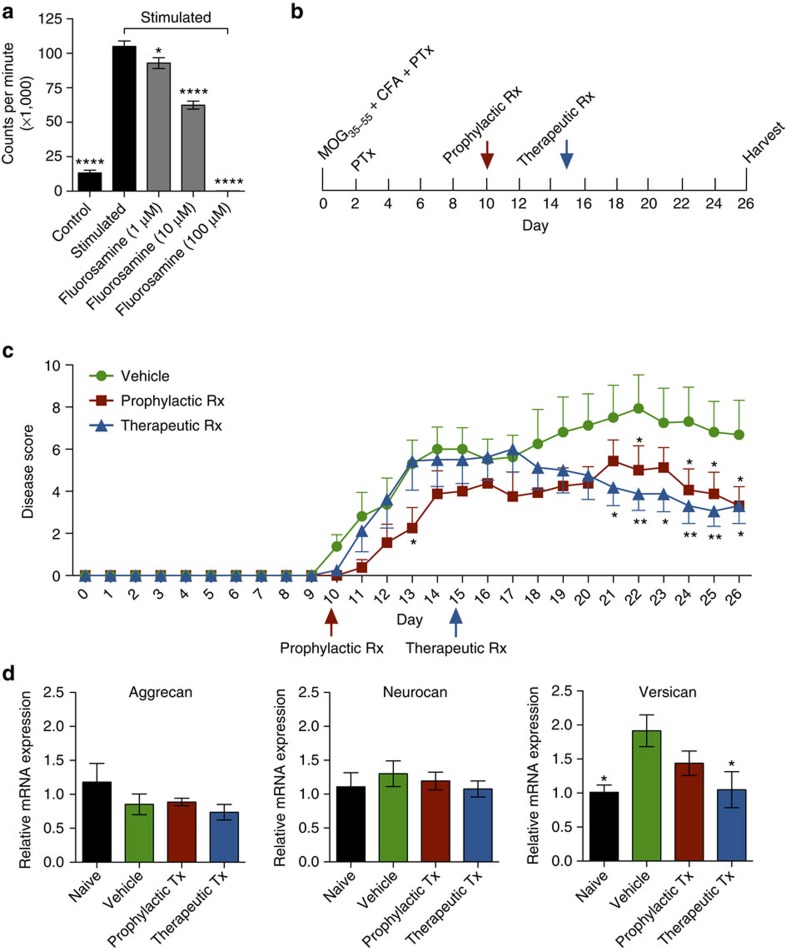
Figure 7. Fluorosamine reduces the proliferation of T cells and ameliorates EAE.
(a) Proliferation of splenocytes activated with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 antibodies is significantly reduced in a concentration-dependent manner by fluorosamine. (b) Schematic for the experimental EAE paradigm and treatment starting points. (c) Disease scores of EAE animals over the course of a 26-day experiment. The animals were treated either prophylactically at day 10 or therapeutically at day 15, compared with vehicle treatment. Both the treatment groups had reduced disease scores on the last few days of the experiment. (d) Isolated RNA from the spinal cords of EAE mice harvested at day 26 shows significant increases in versican in vehicle-treated EAE animals compared with naive subjects, and this is decreased with therapeutic fluorosamine treatment. Results are presented as four replicate wells of an individual experiment conducted twice (a), or from seven to eight animals per group (c,d). MOG, myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein; CFA, Complete Freund's Adjuvant; PTx, pertussis toxin. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ****P<0.0001 one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Dunnett's post hoc test (a,d) or two-way repeated-measures ANOVA with Holm–Sidak's post hoc test (c). Error bars are mean±s.e.m.