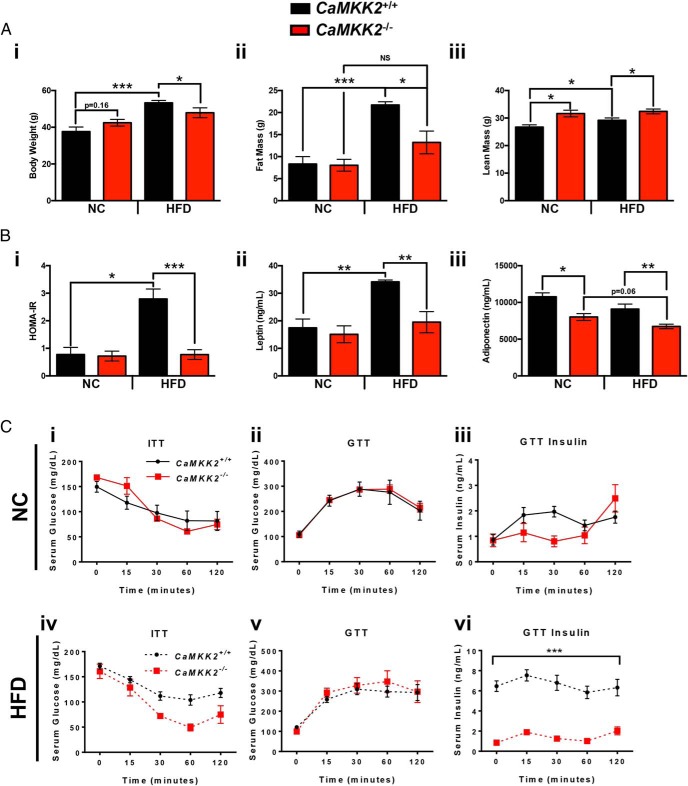
Figure 1.
Loss of CaMKK2 protects against HFD-induced obesity, alters circulating hormone levels, including insulin, and confers protection against insulin resistance. A, Graphical representation of body weight (i), fat mass (ii), and lean mass (iii) measurements from CaMKK2+/+ and CaMKK2−/− male mice fed either NC or HFD. B, HOMA-IR score (i), leptin (ii), and adiponectin (iii) levels from the CaMKK2+/+ and CaMKK2−/− cohorts fed either NC or HFD. C, i and iv, Serum glucose levels in CaMKK2+/+ and CaMKK2−/− mice fed NC (i) and HFD (iv) after an ITT. C, ii, iii, v, and vi, Serum glucose levels (ii and v) and serum insulin levels (iii and vi) in CaMKK2+/+ and CaMKK2−/− mice fed NC (ii and iii) and HFD (v and vi) after a glucose tolerance test (GTT). Data are represented as mean ± SEM. *, P ≤ .05; **, P ≤ .01; ***, P ≤ .001.