Figure 1. Development of an in vitro screening method to identify IN dimerization inhibitors.
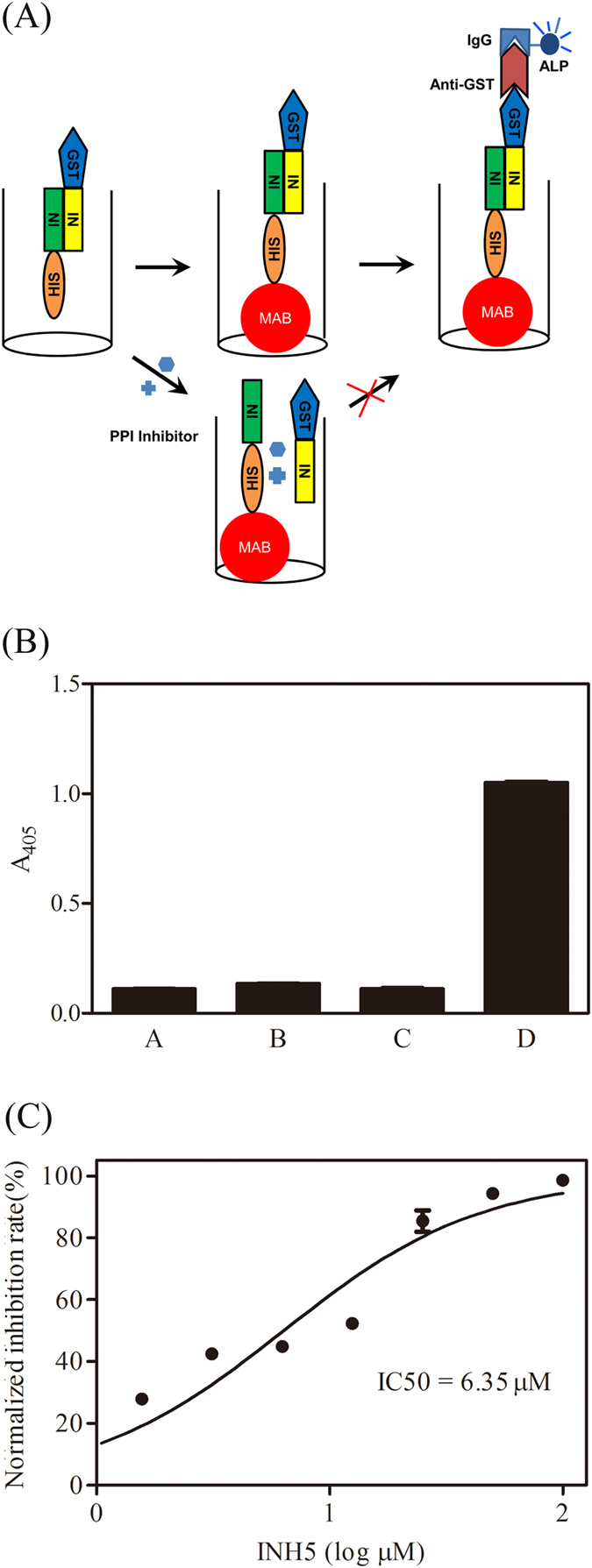
(A) The schemes depict the principle of the assay for IN dimerization. GST–tagged IN (yellow) is mixed with His6-tagged IN (green) at the desired concentrations. Incubation at room temperature allows the formation of GST-IN/His6-IN heterodimers as well as GST-IN and His6-IN homodimers. Then, heterodimers will be captured by Ni2+ -coated magnetic beads (red) through C-terminal His6-tag and detected by alkaline phosphatase conjugated anti-GST antibody (dark red) through its N-terminal GST-tag. Changes in the population of heterodimers due to the presence of modulating compounds will result in an altered output signal and can be picked up. (B) Assay performance under optimal reaction conditions. Bars (A–C) represent signals produced from negative controls in the absence of either GST-IN and His6-IN or GST-IN or His6-IN respectively. Bar D represent signals produced from IN dimerization. (C) Inhibition of IN dimerization by peptide INH5. Error bars represent SD from 3 replicate values.
