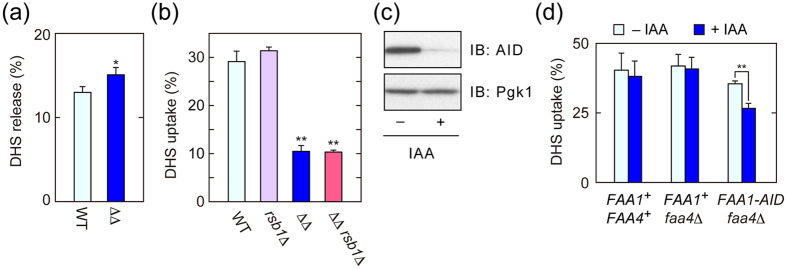
Figure 2. Decreased LCB uptake in faa1Δ faa4Δ cells is not caused by an increase in LCB efflux or change in lipid composition.
(a) BY4741 (wild-type; WT) and AOY13 (faa1Δ faa4Δ; ΔΔ) cells were labeled with [3H]DHS at 30 °C for 5 min. After being washed twice with medium containing BSA, cells with equal radioactivities were suspended in fresh medium containing BSA and incubated at 30 °C for 10 min. Radioactivities associated with cells and medium were counted by a liquid scintillation counter, and those associated with cells are expressed as a percentage of the total radioactivity. Values represent the means ± SDs of three independent experiments, and statistically significant differences are indicated (t-test; *p < 0.05). (b) BY4741, 1825 (rsb1Δ), AOY13, and TNY12 (faa1Δ faa4Δ rsb1Δ) were incubated with 20 μM [3H]DHS at 30 °C for 5 min, and transport activity was determined as in (a). Values represent the means ± SDs of three independent experiments, and statistically significant differences are indicated (t-test; **p < 0.01). (c) TNY34 (faa4Δ FAA1-HA-AID) cells were incubated with 500 μM IAA at 30 °C for 1 hr. Total cell lysates were prepared, separated by SDS-PAGE, and subjected to immunoblotting with anti-AID or, to demonstrate equal protein loading, anti-Pgk1 antibody. IB, immunoblotting. (d) CTY3 (wild-type), TNY32 (faa4Δ), and TNY34 cells were incubated with 500 μM IAA at 30 °C for 1 hr and then treated with 20 μM [3H]DHS for 5 min. Transport activity was determined as in (a). Values represent the means ± SDs of three independent experiments, and statistically significant differences are indicated (t-test; **p < 0.01).