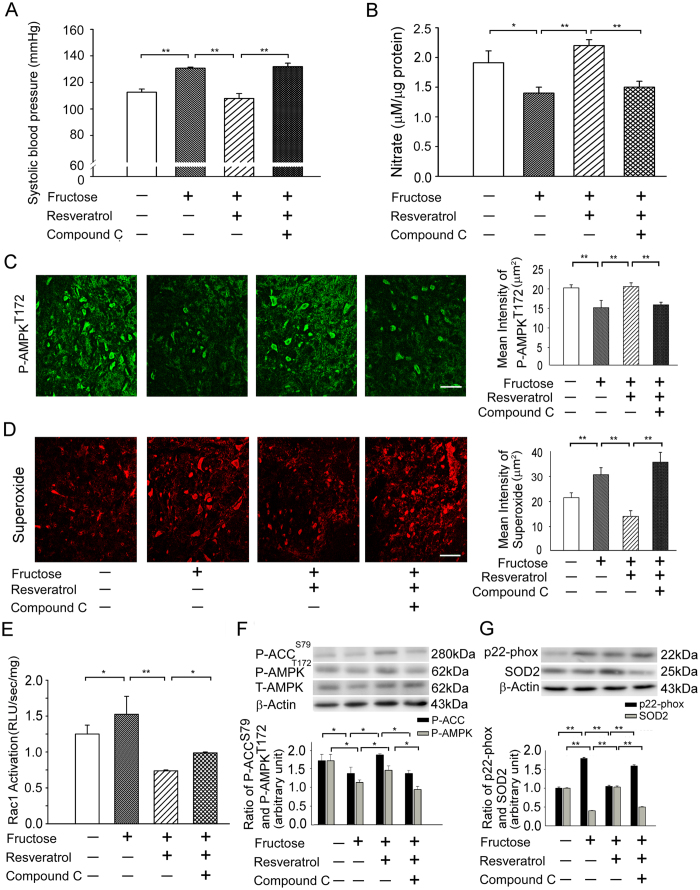
Figure 3. Activation of AMPK abolished the Rac1-induced increases in Rac1 and NADPH oxidase activities and reduced the activities of SOD2 in the RVLM of rats with fructose-induced hypertension.
(A) Graph showing the effects of resveratrol on SBP with or without the administration of compound C. The SBP after treatment with resveratrol was significantly increased by compound C. (B) Levels of NO in the RVLM after the administration of compound C. The bar graph shows that the concentration of NO after treatment with resveratrol was significantly reduced by compound C. (C) Confocal microscopy analysis of green fluorescence was used to estimate p-AMPKT172 levels in the RVLM after treatment with resveratrol and compound (C). The representative images shown demonstrate that the elevation of the AMPK phosphorylation level in the RVLM after treatment with resveratrol was reduced by compound C. (D) Confocal microscopy analysis of DHE-treated brain sections in the RVLM after treatment with resveratrol and compound C. The representative images shown demonstrate that the elevation of the DHE fluorescence level in the RVLM after treatment with resveratrol was reduced by compound C. (E) Bar graph showing the activation ratio of Rac1 after treatment with resveratrol and compound C. The Rac1 activation in the RVLM after treatment with resveratrol was significantly inhibited by treatment with compound C. (F) Immunoblot showing P-ACCS79 and P-AMPKT172 protein levels after treatment with resveratrol and the AMPK inhibitor, compound C. The elevated ACC and AMPK phosphorylation levels in the RVLM after resveratrol treatment were reduced by treatment with compound C. (P-ACCS79, P-AMPKT172 and actin the position of the 280, 62 and 43-kDa molecular weight marker is indicated, respectively) (G) Immunoblot showing p22-phox protein levels after treatment with resveratrol and compound C. The resveratrol-reduced increase in the p22-phox activity ratios in the RVLM were further enhanced by compound C. However, the resveratrol-induced increase in the SOD2 activity in the RVLM was inhibited by compound C. (p22-phox, SOD2 and actin the position of the 22, 25 and 43-kDa molecular weight marker is indicated, respectively) The values are shown as the means ± SEM, n = 6. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. Scale bar: 20 μm.