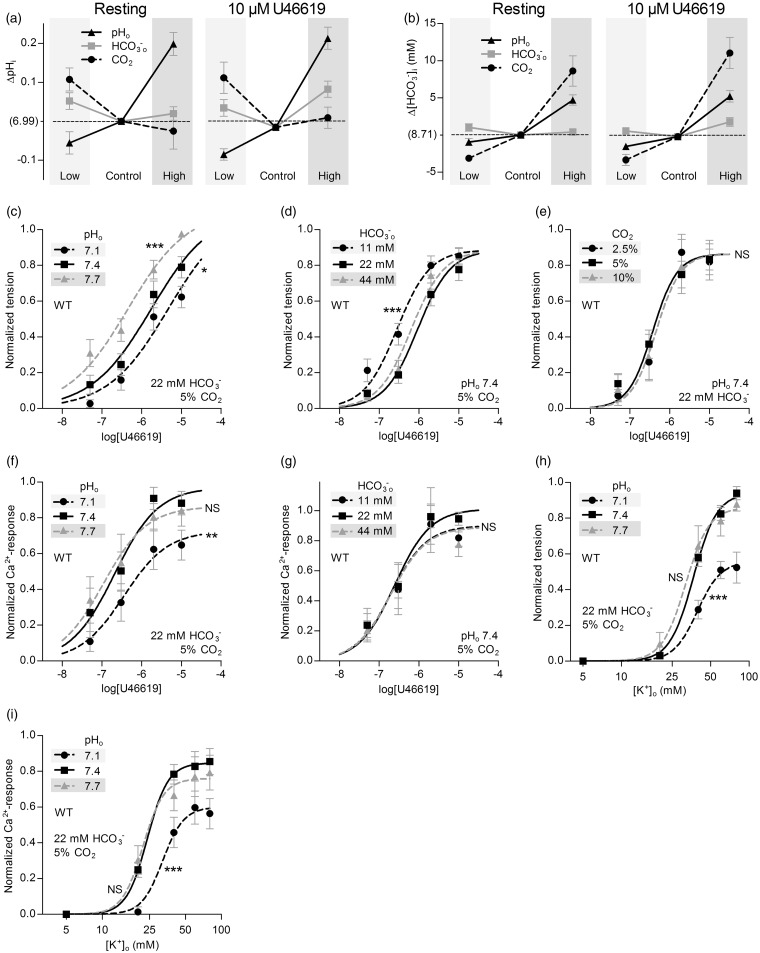
Figure 2.
Selective changes in []o or pHo—but not pCO2—directly modulate basilar artery tone under OOE conditions. (a) Effects of selectively varying pHo, []o or pCO2 (maintaining other two at control levels) on VSMC pHi in resting basilar arteries (left panel) or basilar arteries contracted by 10 µM U46619 (right panel). Under “Control” conditions, CO2 is 5%, pHo 7.4, and []o 22 mM. Compared to “Control”, “Low” refers to selective changes in CO2 to 2.5%, []o to 11 mM or pHo to 7.1, and “High” refers to selective changes in CO2 to 10%, []o to 44 mM or pHo to 7.7. Arteries are from wild-type mice (n = 6). (b) Effects of selectively varying pHo, []o or pCO2 (maintaining other two at control levels) on VSMC calculated []i in resting (Continued) Figure 2. Continue. basilar arteries (left panel) or basilar arteries contracted by 10 µM U46619 (right panel). Arteries are from wild-type mice (n = 6). (c-e) Effects of selectively varying pHo, []o, or pCO2 (maintaining other two at control levels) on U46619-induced tension development in basilar arteries from wild-type mice (n = 12 or 13). (f, g) Effects of selectively varying pHo or []o (maintaining unvaried parameters at control levels) on U46619-induced VSMC Ca2+-responses in basilar arteries from wild-type mice (n = 6 for both). (h) Effects of selective changes in pHo ([]o=22 mM, CO2=5%) on depolarization-induced tension development of basilar arteries from wild-type mice (n = 8). We induce depolarization by raising [K+]o. (i) Effects of selective changes in pHo ([]o=22 mM, CO2=5%) on depolarization-induced VSMC Ca2+ responses in basilar arteries from wild-type mice (n = 7). The curves in panels (c) through (i) are the results of least-squares fits to sigmoidal functions, and we compare them using extra sum-of-squares F-tests. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, NS: not significantly different vs. control conditions (pHo=7.4, []o=22 mM, CO2=5%).