FIGURE 8.
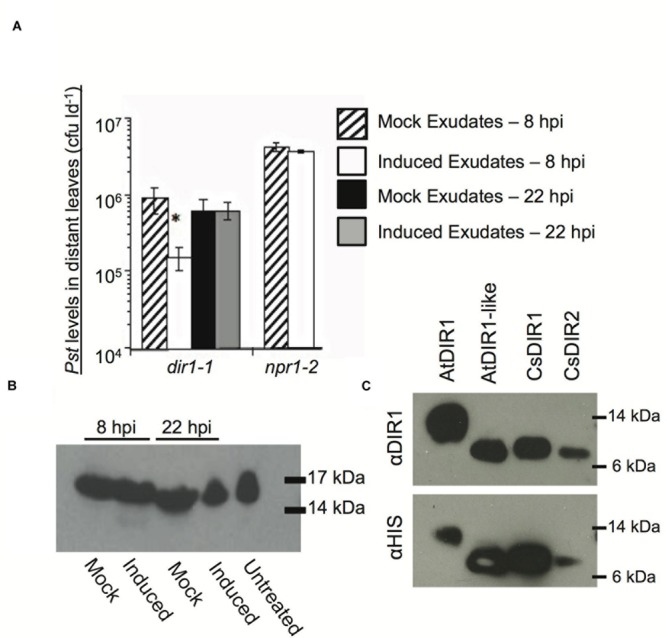
Characterization of DIR1-mediated SAR in Cucumis sativus. (A) SAR-induced cucumber exudates rescue the SAR defect in dir1-1. Petiole exudates were collected from cut cucumber ends at 8 or 22 hpi with 10 mM MgCl2 (mock) or SAR-inducing (induced) Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae D20. Exudates from Mock (8 or 22 hpi) or SAR-induced (8 or 22 hpi) were infiltrated into 2 dir1-1 or npr1-2 leaves. Two days later distant leaves were inoculated with virulent Pst (105 cfu ml-1) and 3 dpi Pst levels were measured. An asterisk (∗) indicates a significant difference between plants infiltrated with mock and induced exudates. (B) A DIR1-sized band is present in cucumber phloem before and after SAR induction Exudates were lyophilized and subjected to immunoblot analysis using the DIR1 antibody. 17 and 14 kDa protein molecular weight markers are indicated. (C) Recombinant CsDIR1 and CsDIR2 protein is detected by the polyclonal DIR1 antibody. Immunoblots of crude extracts from IPTG-induced Rosetta-gami strains expressing His-tagged AtDIR1, AtDIR1-like, CsDIR1, and CsDIR2 proteins using anti-DIR1 or anti-HIS antibodies. (A) Was repeated two additional times, (B,C) were repeated once, all with similar results.
