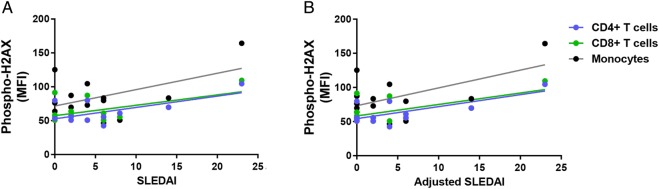
Figure 2.
Correlation between disease activity and phospho-H2AX levels in primary CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells and monocytes from patients with SLE (n=12, 14 and 14, respectively). (A) SLEDAI scores were positively correlated with phospho-H2AX levels in primary CD4+ T cells and CD8+ T cells from patients with SLE (p=2.88×10−2and 4.20×10−2, respectively), but statistical significance was not reached in monocytes (p=6.24×10−2). (B) Adjusted SLEDAI scores, which excluded scoring criteria for low complement levels and increased anti-dsDNA antibodies, were positively correlated with phospho-H2AX levels in SLE CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells and monocytes (p=1.14×10−2, 1.79×10−2 and 3.38×10−2, respectively). Phospho-H2AX levels were measured by flow cytometry, and are provided as MFIs (mean±SEM). MFI, median fluorescence intensity; phospho-H2AX, phosphorylated H2AX; SLE, systemic lupus erythematosus; SLEDAI, SLE disease activity index.