Figure 4.
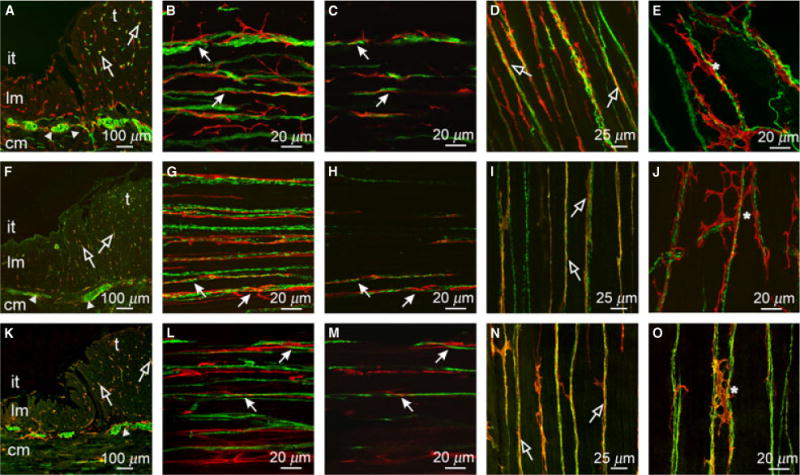
Relationship between enteric neurons and ICC within the taenia (t) and inter-taenia (it) regions of the proximal colon. (A,F,K) Cryostat cross-sections of PGP9.5+, sub-P and nNOS containing neurons (green) with Kit+ ICC (red), respectively. Close appositions are seen in the CM and taenia region of the colon (open arrows). (B,C) CM (cm in A,F,K) double labeled with PGP9.5 (green) and Kit (red). (G,H) CM double labeled with sub-P and Kit. (L,M) CM double labeled with nNOS and Kit. (C,H,M) Single sections of reconstructed stacks taken from (B,G,L). ICC ran parallel to and in close apposition with excitatory and inhibitory neurons. (D,I,N) & (E,J,O) Taenia LM and serosal surface of taenia double labeled with PGP9.5 (D,E), sub-P (I,J) and nNOS (N,O) and Kit, respectively. Enteric nerve fibers formed close anatomical associations with ICC throughout the taenia. ICC were observed to form an anastomosing network (*) along and between nerve fibers adjacent to the serosa of the taenia. Scale bars are as indicated in each panel.
