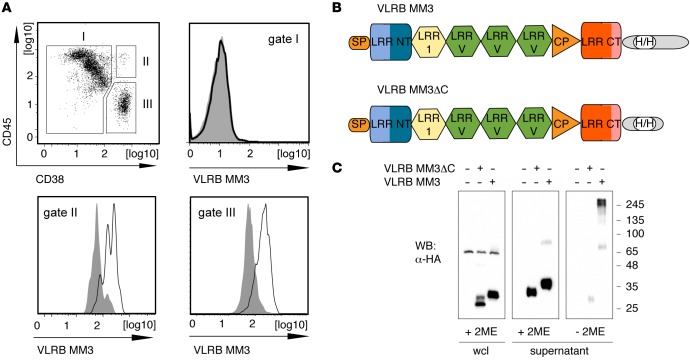
Figure 1. Isolation of monoclonal VLRB MM3.
(A) BM aspirate from a patient with multiple myeloma was stained with VLRB MM3 containing culture supernatant from transiently transfected HEK293T cells. The cells were costained for CD38 and CD45 expression and separated into non-PCs (gate I, CD38–/lo), nonmalignant PCs (gate II, CD45+/CD38++), and malignant PCs (gate III, CD45–/lo/CD38++). Histograms depict VLRB MM3 reactivity within the indicated gates. VLRB MM3 signals are indicated by solid black lines, and negative control VLR4 signals are shown as solid gray histograms. (B) Structural characteristics of VLRB MM3. Individual VLRB MM3 units consist of a signal peptide (SP), N-terminal LRR (LRR NT), LRR-1, three variable LRRv units, a connecting peptide, C-terminal capping LRR (LRR CT), and the invariable stalk region. Location of engineered sequences encoding the HA- and 6xHis epitope tags (H/H) into the stalk region are indicated. (C) Western blot (WB) analysis of WCLs and supernatants of HEK293T cells transiently transfected with VLRB MM3 and the multimerization-deficient mutant VLRB MM3ΔC. The samples were separated by SDS-PAGE under reducing and nonreducing conditions, and recombinant VLRB protein was detected with Abs specific to the HA-epitope tag. LLR, leucine-rich repeat; PCs, plasma cells; VLRB, variable lymphocyte receptor B; WCLs, whole-cell lysates.