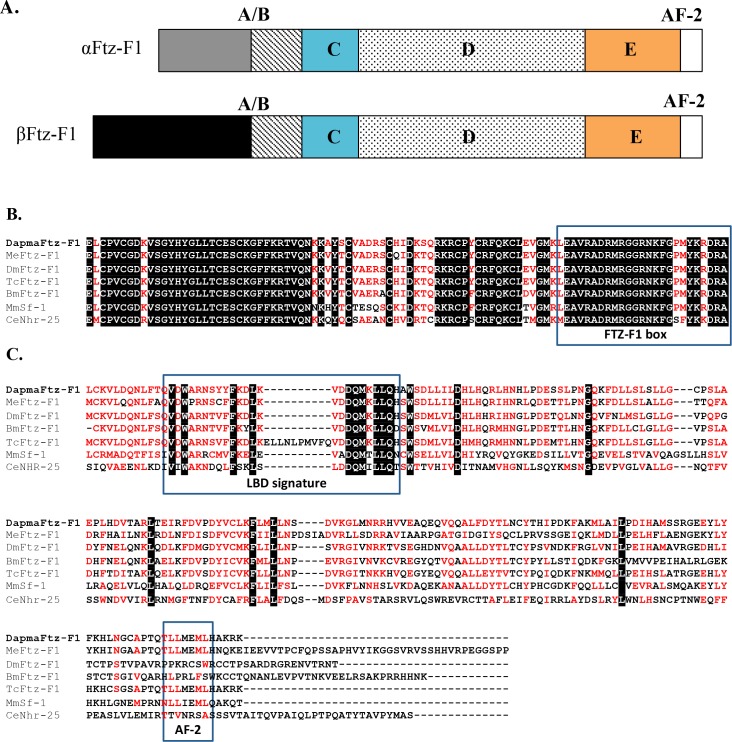
Fig 2. Evolutionary conserved domains of D. magna Ftz-F1.
(A) Schematic diagram of the Ftz-F1 regions that are divided into A/B, C, D and E regions. (B) Alignment of the C region and the Ftz-F1 box (boxed), and (C) alignment of the E region showing the LBD signature domain (boxed) and AF-2 motif (boxed). Identical amino acids are shaded in black whereas amino acids with similar characteristics are colored in red. MeFtz-F1 is the Me. ensis (shrimp) protein; DmFtz-F1 is the Dr. melanogaster (fruit fly) protein; BmFtz-F1 is the B. mori (silkworm) protein; and TcFtz-F1 is the T. castaneum (beetle) protein. MmSf-1 is the steroidogenic factor-1 of Mu. musculus (mouse); and CeNhr-25 is the nuclear hormone receptor-25 of C. elegans (roundworm).