Figure 1. Synaptic transmission is homeostatically regulated.
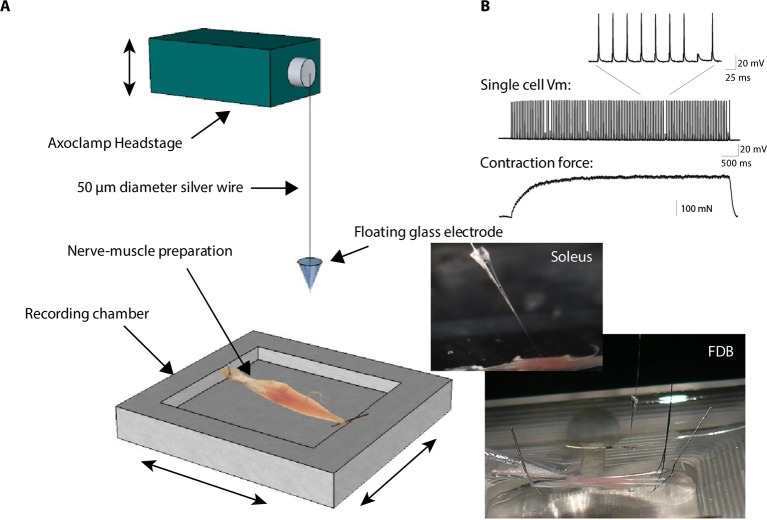
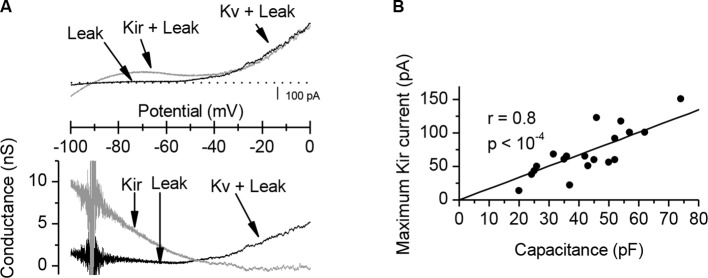
(A) Perforated patch-clamp on Xenopus neuron (N) and muscle cell (M) in primary culture. Presynaptic APs were triggered with current steps. Postsynaptic APs were recorded under current-clamp and nicotinic synaptic currents under voltage-clamp (-80 mV). (B) Intracellular recording in soleus muscle fibers from an adult mouse using a floating sharp electrode (see Materials and Methods and Figure 1—figure supplement 1). (C) Nicotinic conductance calculated from averaged ePSCs (n = 30 ePSCs for each dot) in different Xenopus muscle cells as a function of their input conductance. The black line shows the linear regression. (D) In mice, membrane potential reached by the ePSP in individual FDB muscle fibers after treatment with µ-conotoxin GIIIB, in absence of burst stimulation of the nerve (black dots, n= 88 fibers, 2 muscles, 2 mice), and in test preparations (grey dots, n = 108 fibers, 2 muscles, 2 mice) for which the nerve was burst stimulated prior to conotoxin treatment (15 bursts in 10 min, each of 120 events at 30 Hz). (E) Mean synaptic gain at Xenopus synapses (dots, n = 5 synaptic connections) and in mouse neuromuscular junctions (squares, n = 4 muscle fibers from different mice) during chronic bursts of presynaptic stimulation (bursts of 80 to 120 pulses, 30 Hz for 30 min).
Figure 1—figure supplement 1. Floating electrode.
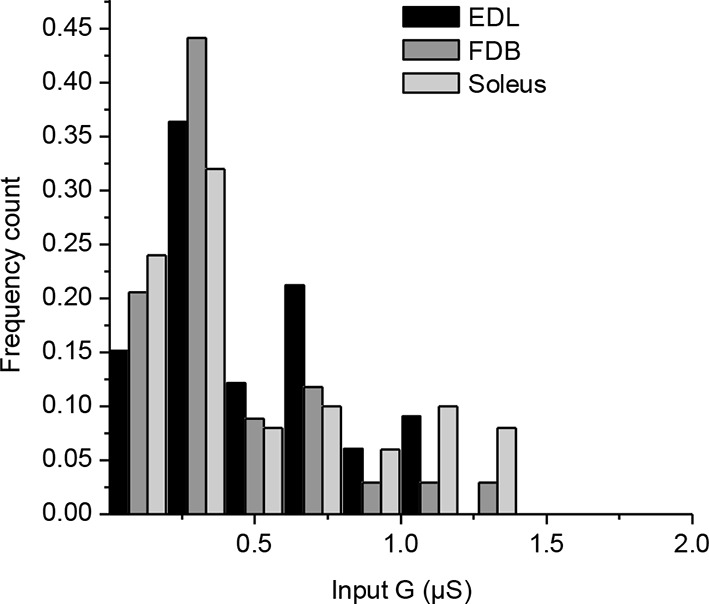
Figure 1—figure supplement 2. Mouse muscles fibers have a wide range of input conductances.