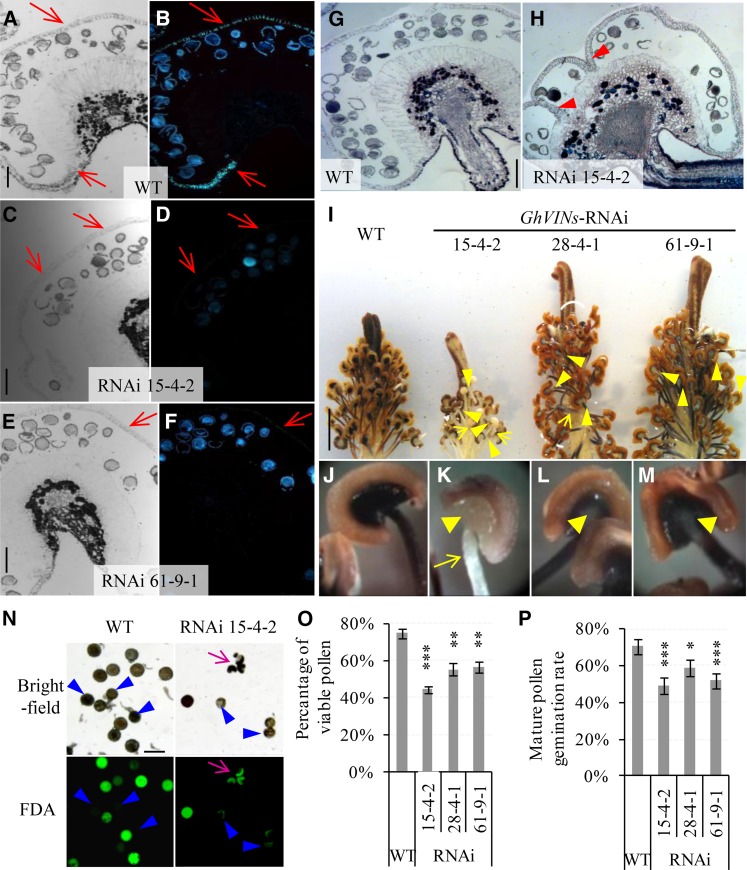
Figure 4.
GhVIN1-RNAi lines displayed unthickened endothecium walls, incomplete septum degradation in a certain number of −1-d anthers, reduced starch accumulation in −1-d stamens, and lowered pollen viability and pollen tube germination rates. A to F, Representative images of −1-d wild-type (WT; A and B), RNAi 15-4-2 (C and D), and RNAi 61-9-1 (E and F) anther sections stained with Aniline Blue, observed under bright field (A, C, and E) and UV light (B, D, and F). Red arrows indicate the position of the anther wall. G and H, Representative images of −1-d wild-type (G) and RNAi 15-4-2 (H) anther sections stained with Toluidine Blue. Note the remaining septum (arrowheads in H) but its absence in G. I, Representative image of wild-type and transgenic −1-d stamens and styles stained with KI-I2. J to M, Magnified views of stamen from the wild type (J), RNAi 15-4-2 (K), RNAi 28-4-1 (L), and RNAi 61-9-1 (M), respectively. Compared with the strong staining of starch in the wild-type stamen by KI-I2, indicated by the dark color, the transgenic stamen exhibited much weaker staining in filaments and especially at the anther-filament joint regions (yellow arrow and arrowheads, respectively). N, Bright-field and green fluorescence images of the same set of mature pollen grains stained with FDA from the wild type and RNAi line 15-4-2. Pink arrows indicate malformed pollen grains. Blue arrowheads point to pollen grains with lost viability. O, The proportions of viable pollen grains determined by FDA staining were reduced significantly in the transgenic lines compared with the wild type. Each value is the mean ± se from four biological replicates. P, Pollen germination rates were reduced significantly in the GhVIN1-RNAi lines compared with the wild type. Each value is the mean ± se of eight flowers from four plants for each line. Asterisks indicate significant difference between RNAi and wild-type plants based on one-way ANOVA after arcsine transformation (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; and ***, P < 0.001). Bars = 100 μm in A, C, E, G, and N and 1 cm in I. The scales in B, D, F, and H are the same as those in A, C, E, and G, respectively.