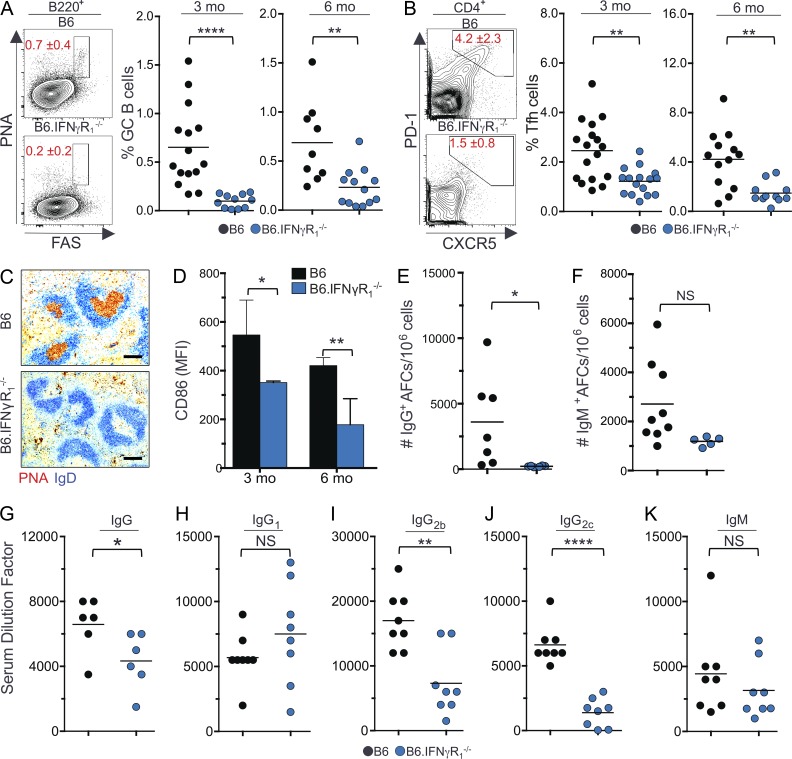
Figure 1.
IFN-γR signaling is required for Spt-GC formation and IgG production. (A and B) The percentages of B220+FashiPNAhi GC B cells (A) and CD4+CXCR5hiPD-1hi Tfh cells (B) were obtained from flow cytometric analysis of spleen cells of 3- and 6-mo-old B6 and B6.IFN-γR1−/− mice. Each symbol represents a mouse (n = 11–15). (C) Representative histological images of spleen sections from 6-mo-old mice (n = 5 per group) stained with the GC B cell marker PNA and anti-IgD. Bars, 150 µm. (D) Flow cytometric analysis of CD86 expression (MFI) on total B220+ B cells at 3 and 6 mo of age (n = 5 mice per group). Error bars are mean ± SD. (E and F) Numbers of IgG+ (E) and IgM+ (F) splenic AFCs in 6-mo-old mice of indicated strains (n = 5–9). (G–K) Analysis of serum titers of IgG, IgG1, IgG2b, IgG2c, and IgM Abs in 6-mo-old mice by ELISA. Each symbol represents a mouse (n = 6–8). The data shown are the cumulative results of two or three independent experiments. Statistical values were determined using an unpaired, nonparametric, Mann–Whitney Student’s t test. Horizontal lines indicate mean values. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ****, P < 0.001.