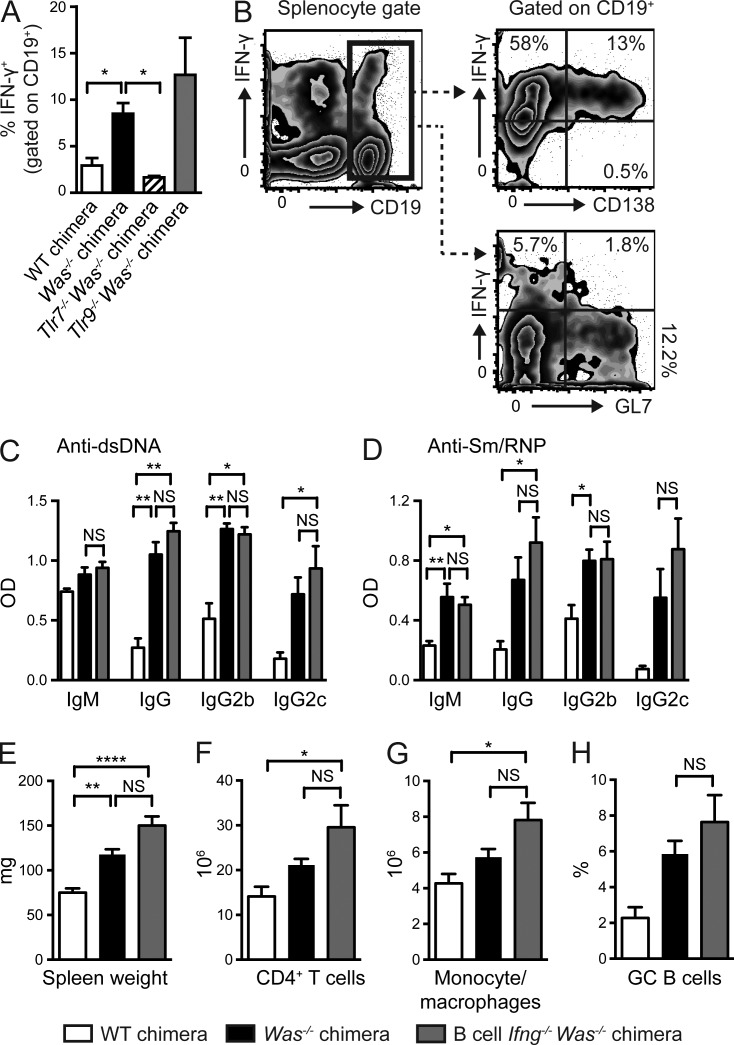
Figure 6.
B cell–derived IFN-γ is not required for systemic autoimmunity. (A) Percentage IFN-γ+ B cells (gated on CD19+) in WT, Was−/−, and B cell–intrinsic Tlr7−/− and Tlr9−/− chimeras. (B) Representative flow plots demonstrating expression of the plasma cell marker, CD138, but not the GC B cell marker, GL7, on IFN-γ–producing CD19+ B cells. (C and D) Anti-dsDNA (C) and Sm/RNP (D) auto-Ab titers at 12 wk after transplantation. (E–H) Spleen weight (E) and the number of CD4+ T cells (F) and CD11b+GR1lo monocyte/macrophages (G), as well as the percentage of PNA+FAS+ GC B cells (H). Data are representative of two WT (n = 5), two Was−/− (n = 11), two B cell Ifng−/− Was−/− (n = 11), two Was−/−.Tlr7−/− (n = 14), and two Was−/−.Tlr9−/− (n = 15) chimeras sacrificed 24 wk after transplantation. (A and C–H) Error bars indicate SEM. (A) *, P < 0.05 for each experimental group relative to Was−/− chimera controls by the Mann-Whitney U-test. (C–H) *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ****, P < 0.0001, by the Kruskal-Wallis one-way ANOVA.