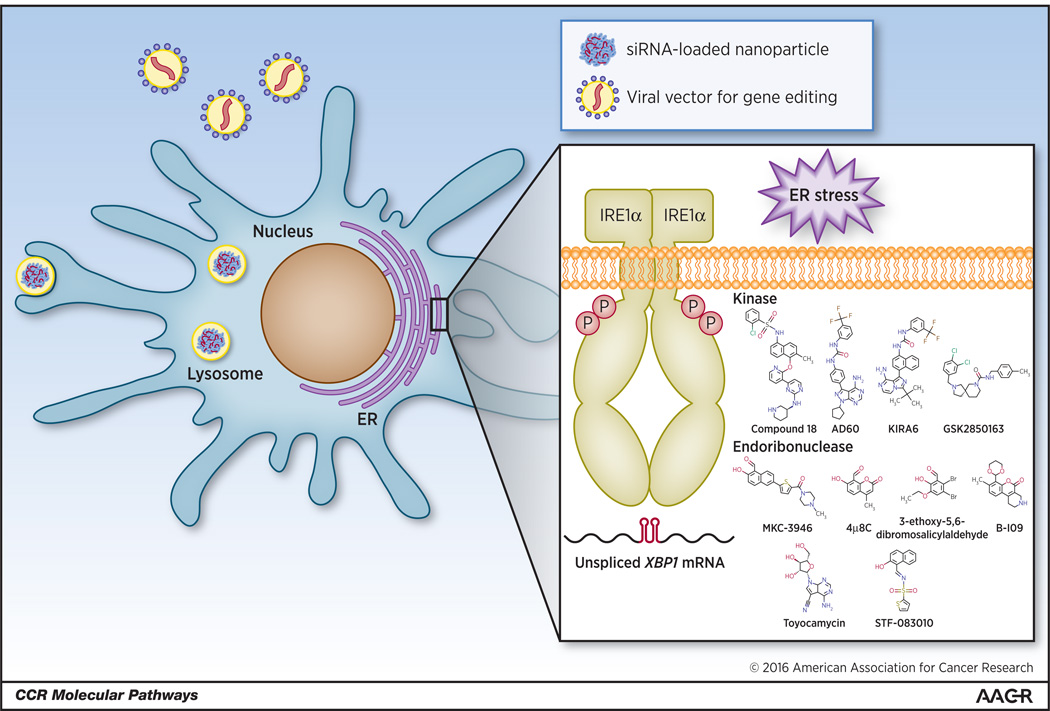
Figure 2. Potential therapeutic strategies for targeting IRE1α-XBP1 signaling in cancer-associated DCs.
The IRE1α kinase and endoribonuclease domains can be individually blocked with small molecules. Additionally, the constitutive activation of either XBP1 or IRE1α can be reduced using nanoparticles encapsulating siRNAs. In terms of DC-based vaccines or autologous DC transfer, IRE1α or XBP1 could be selectively ablated ex vivo through the use of virally-delivered DNA editing technologies such as zinc finger nucleases, TALENs, and CRISPR/CAS9. Genome edited DCs could then be transplanted back into patients to enhance standard therapeutic regimes.