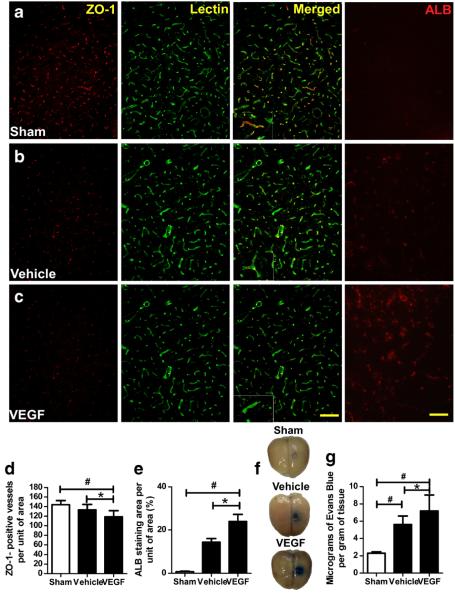
Fig. 2.
VEGF increases blood–brain barrier permeability. a–c Immunofluorescence staining of ZO-1-positive vessels and albumin (ALB) in the striatum 6 h after VEGF injection. Images are shown at ×200 magnification. Scale bar=50 μm. d–e Quantification showed that VEGF-treated 2VO rats had fewer ZO-1-positive (red) vessels (green; d) and higher albumin staining (e) than did sham and vehicle-treated groups. *p<0.05 vs. vehicle group; #p<0.05 vs. sham group; n=8/group. f Representative rat brains from each group 30 min after Evans Blue administration. g Quantification showed that VEGF significantly increased the amount of extravasated Evans Blue dye compared with that in the other two groups. *p<0.05 vs. vehicle; #p<0.05 versus sham. n=8/group. Values are mean±SD