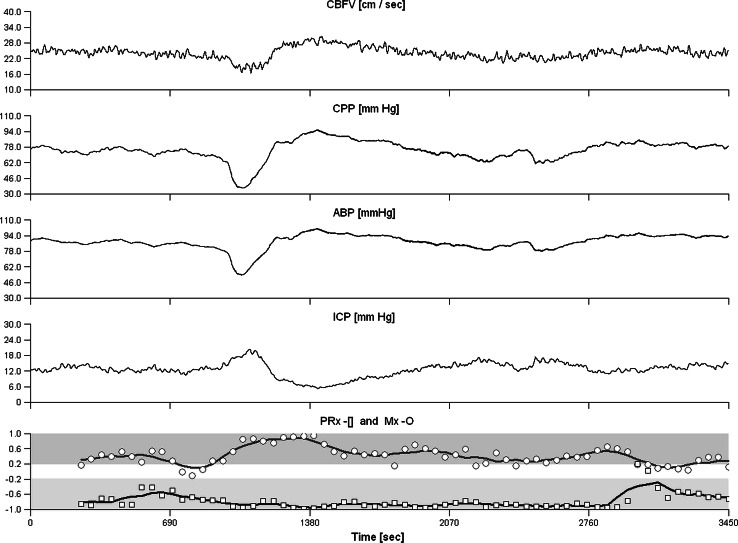
Fig. 2.
Signal recording of a 71-year-old patient with hemorrhagic stroke, heart failure, and a 3-month outcome mRS score of 4. CBFV, ABP and ICP have been recorded for 3450 s. CPP was calculated by ABP–ICP. In the lower channel, signal correlation coefficients are indicated either by circles (between CBFV and CPP, for Mx calculation) or by squares (between ABP and ICP, for PRx calculation) and moving average curves of five consecutive correlation coefficients are drawn. The signals CBFV and CPP showed strictly parallel fluctuations, while signal changes of ABP and ICP were clearly opposed. Accordingly, the indexes strongly differed: Mx was 0.31, indicating impaired CA, while PRx was −0.77, indicating intact cerebrovascular reactivity. The moderately severe outcome (mRS score = 4) better fits to the Mx value. ABP arterial blood pressure, CA cerebral autoregulation, CPP cerebral perfusion pressure, CBFV cerebral blood flow velocity, ICP intracranial pressure, mRS modified Rankin Scale