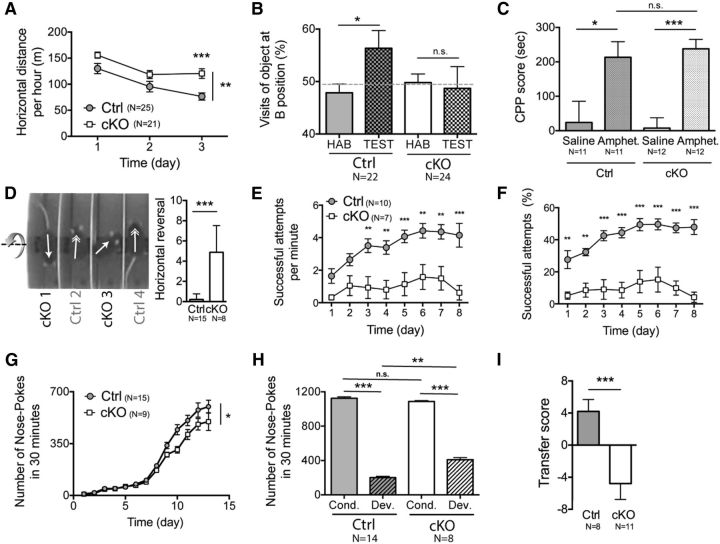
Figure 6.
Habituation and learning are altered in mice depleted of NMDA-R in iMSNs. A, One hour open-field activity analyzed in cKO and A2Acre−/−Grinlox/loxRosa26-YFP (control, Ctrl) mice shows an increase in the total horizontal distance run by cKO mice at day 3. B, Habituation is impaired in cKO mice during the novel object recognition task (HAB, habituation phase; TEST, test phase). C, CPP is not altered in cKO mice, confirming that the visual memory of the cKO is functional. D, During the accelerating rotarod task, cKO mice (i.e., cKO 1) reversed horizontally (180°) and continued the walk backwards, in contrast to control mice, which kept the same walk orientation. Arrows indicate the walking orientation of each mouse. The number of horizontal reversals (180°) accomplished by cKO mice is significantly higher than in Ctrl. E, F, The average speed of success (F) as well as the average success rates over time from the same group of mice presented in E during the training period of the single-pellet reaching task are significantly higher for the Ctrl mice than for the cKO mice. The cKO mice are not able to learn the task because there is no effect of the time on their speed of success or their rate of success. G, Mice were trained in a Skinner box to do an NP to obtain a food pellet with a first period of fixed ratio (starting with 1:1, ending with 10:1) followed by a variable ratio (starting with ±10:1, ending with ±20:1) schedule. Conditioned instrumental reinforcement with a fixed ratio schedule reveals impaired attribution of NP to a reward in cKO animals during this initial learning phase (days 1–13). H, After 25 d of learning, cKO and Ctrl mice reached a plateau for 3 d (Cond.), which was not different between the two groups, whereas, afterward, the devaluation was significantly lower for cKO mice because the NP level was significantly higher. I, During the PIT, the Ctrl mice exhibited a significantly higher lever press rate when the stimulus predicted the same outcome as the response than when the stimulus predicted a different outcome, whereas cKO mice displayed unspecific lever pressing.