Fig. 1.
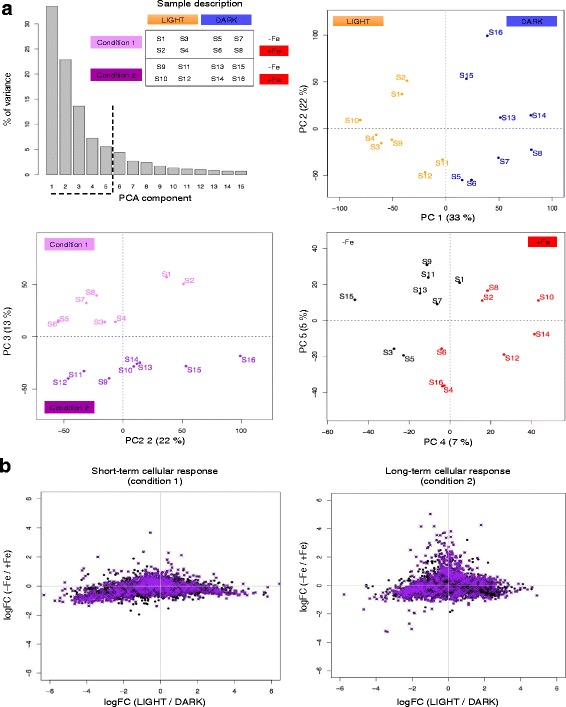
Global analysis of changes in mRNA abundance. Gene expression data for all genes and all samples were analyzed by PCA. PCA is a well-established technique in multivariate statistics. The general principle is to determine new coordinate systems such that the first coordinate explains the maximal amount of variance in the data and successive coordinates explain maximal remaining variance whilst being orthogonal to the first [16]. a Barplot showing the variability accounted for by each PCA component. Components 1 and 2 accounted for 33 and 22 % of the global variance, respectively. Components 3, 4 and 5 accounted for 13, 7 and 5 % of the global variance. Biplots representing the RNAseq samples on the coordinate systems defined by PCA components 1 and 2 (upper right), PCA components 2 and 3 (lower left) and PCA components 4 and 5 (lower right). b Plots of LogFC values calculated with gene expression measurements for LIGHT and DARK samples (x-axis) or for –Fe and + Fe samples (y-axis). Points represent genes. Positive LogFC values on the x-axis indicate higher levels of gene expression in the light than in the dark,, whereas positive LogFC values on the y-axis indicate higher levels of gene expression –Fe than in + Fe conditions. The 1049 genes selected for further characterization are shown in purple (see the main text and Additional file 4: Data Sets 1)
