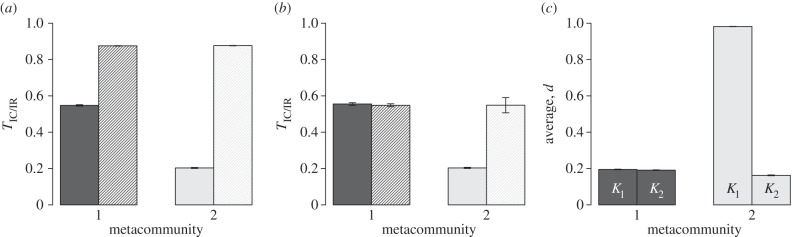
Figure 3.
Analysis of dispersal pattern in symmetric (1) and asymmetric (2) metacommunities. (a) Testing TIC/IR using full permutation of individual positions. Bars represent observed (plain bars) and randomized values (striped bars) of TIC/IR at generation 20 000 averaged over 100 independent simulations. Results for both metacommunity 1 (dark grey bar) and 2 (light grey bar) are shown. For each bar, a 95% CI based on central limit theorem is provided. (b) Similar to panel (a), but overlooking intraspecific variability and permuting only species dispersal values. (c) Average dispersal value in small (bars labelled ‘K1’) and large (bars labelled ‘K2’) communities for metacommunity 1 (dark grey) and 2 (light grey). 95% CI of these average value based on central limit theorem approximation are reported for each bar. Testing whether mean dispersal was higher in small communities yielded that the observed difference is statistically significant in both metacommunitites (test based on the central-limit theorem normal approximation; p = 0.0001 in metacommunity 1, p < 10−12 in metacommunity 2).