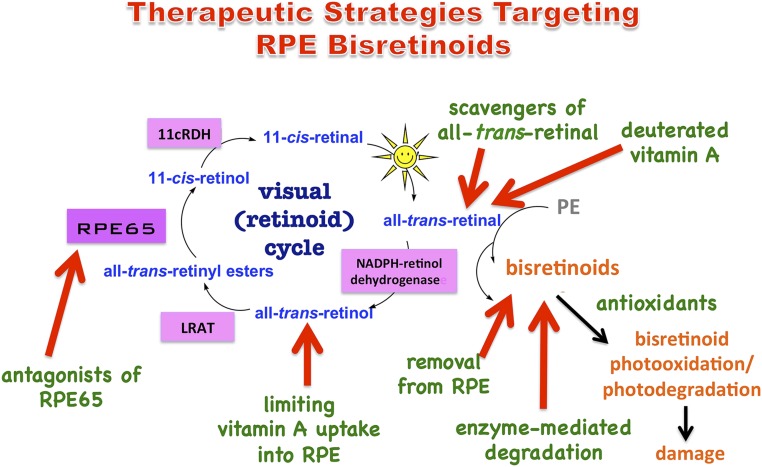
Fig. 1.
Therapeutic strategies targeting RPE bisretinoids. Bisretinoids are visual cycle adducts having a variety of structures. These fluorophores form randomly in photoreceptor cell outer segments due to reactions of retinaldehyde (all-trans- and 11-cis-retinal) with amines such as PE. Bisretinoids are transferred to RPE by phagocytosis and accumulate as lipofuscin. Vitamin A (all-trans-retinol) enters the visual cycle by uptake into RPE. On photoisomerization of 11-cis-retinal in photoreceptor cells, all-trans-retinal is released from rhodopsin and is reduced to all-trans-retinol by NADPH-dependent all-trans-retinol dehydrogenase (NADPH-retinol dehydrogenase). Within RPE, LRAT converts all-trans-retinol to all-trans-retinyl esters; the isomerase RPE65 generates 11-cis-retinol, and 11-cis-retinol is oxidized to 11-cis-retinal by 11-cis-retinol dehydrogenase (11-cRDH). Bisretinoids are photosensitizers; they also photooxidize and photodegrade, releasing damaging dicarbonyls and aldehyde-containing fragments.